Research Success Stories
Indoor localization is an active area of research dominated by traditional machine-learning techniques. Deep learning-based systems have shown unprecedented improvements and have accomplished exceptional results over the past decade, especially the Transformer network within natural language processing (NLP) and computer vision domains. We propose the hyper-class Transformer (HyTra), an encoder-only Transformer with multiple classification heads (one per class) and learnable embeddings, to investigate the effectiveness of Transformer-based models for received signal strength (RSS) based WiFi fingerprinting. HyTra leverages learnable embeddings and the self-attention mechanism to determine the relative position of the wireless access points (WAPs) within the high-dimensional embedding space, improving the prediction of user location. From an NLP perspective, we consider a fixed order sequence of all observed WAPs as a sentence and the captured RSS value(s) for every given WAP at a given reference point from a given user as words. We test our proposed network on public and private datasets of different sizes, proving that the quality of the learned embeddings and overall accuracy improves with increments in samples.
Posted on: March 2023
Authored: Tong Boon Tang
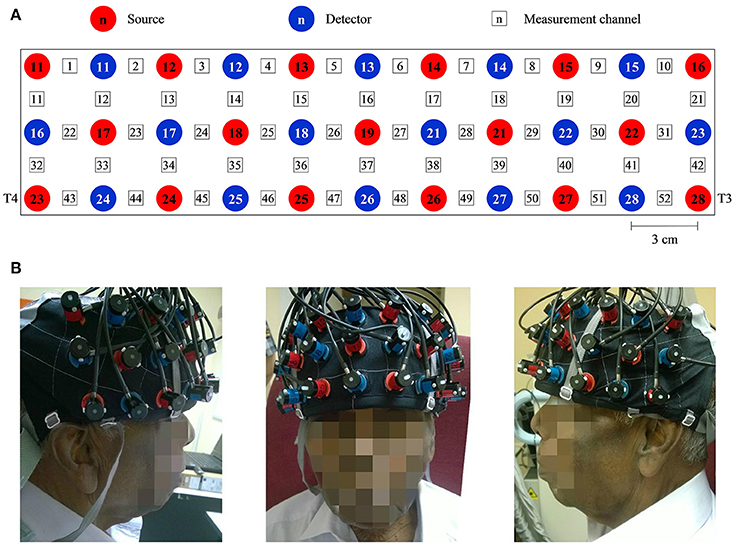
Cognitive performance is relatively well preserved during early cognitive impairment owing to compensatory mechanisms. We explored functional near-infrared spectroscopy (fNIRS) alongside a semantic verbal fluency task (SVFT) to investigate any compensation exhibited by the prefrontal cortex (PFC) in Mild Cognitive Impairment (MCI) and mild Alzheimer's disease (AD). In addition, a group of healthy controls (HC) was studied. A total of 61 volunteers (31 HC, 12 patients with MCI and 18 patients with mild AD) took part in the present study. Although not statistically significant, MCI exhibited a greater mean activation of both the right and left PFC, followed by HC and mild AD. Analysis showed that in the left PFC, the time taken for HC to achieve the activation level was shorter than MCI and mild AD (p = 0.0047 and 0.0498, respectively); in the right PFC, mild AD took a longer time to achieve the activation level than HC and MCI (p = 0.0469 and 0.0335, respectively); in the right PFC, HC, and MCI demonstrated a steeper slope compared to mild AD (p = 0.0432 and 0. 0107, respectively). The results were, however, not significant when corrected by the Bonferroni-Holm method. There was also found to be a moderately positive correlation (R = 0.5886) between the oxygenation levels in the left PFC and a clinical measure [Mini-Mental State Examination (MMSE) score] in MCI subjects uniquely. The hyperactivation in MCI coupled with a better SVFT performance may suggest neural compensation, although it is not known to what degree hyperactivation manifests as a potential indicator of compensatory mechanisms. However, hypoactivation plus a poorer SVFT performance in mild AD might indicate an inability to compensate due to the degree of structural impairment. Consistent with the scaffolding theory of aging and cognition, the task-elicited hyperactivation in MCI might reflect the presence of compensatory mechanisms and hypoactivation in mild AD could reflect an inability to compensate. Future studies will investigate the fNIRS parameters with a larger sample size, and their validity as prognostic biomarkers of neurodegeneration.
Posted on: September 2017
Authored: Tang Tong Boon
Mismatch between mental workload and working memory capacity can cause mental underload or overload. Adopting the Yerkes-Dodson law as the framework, functional near-infrared spectroscopy adaptive cognitive training system (FACTS) has been developed, whereby the mental workload shall never exceed an individual's capacity, to prevent those unintended conditions. It works by monitoring mental workload in real time and performing dynamic difficulty adjustment accordingly. The feasibility study involved thirty-seven healthy participants undergoing mental arithmetic task with and without FACTS. Without FACTS, the participants not only showed higher NASA Task Load Index scores but also poorer task performance and a significant drop in DLPFC activation towards the end of the task, signifying more severe mental overload. Conversely, they continued to exhibit manifestation of productive learning with FACTS despite showing early signs of mental overload. The study results demonstrated that it is feasible to implement the concept of FACTS. The actual gains from cognitive training will be investigated in future longitudinal study.
Posted on:September 2020
Authored: Tang Tong Boon
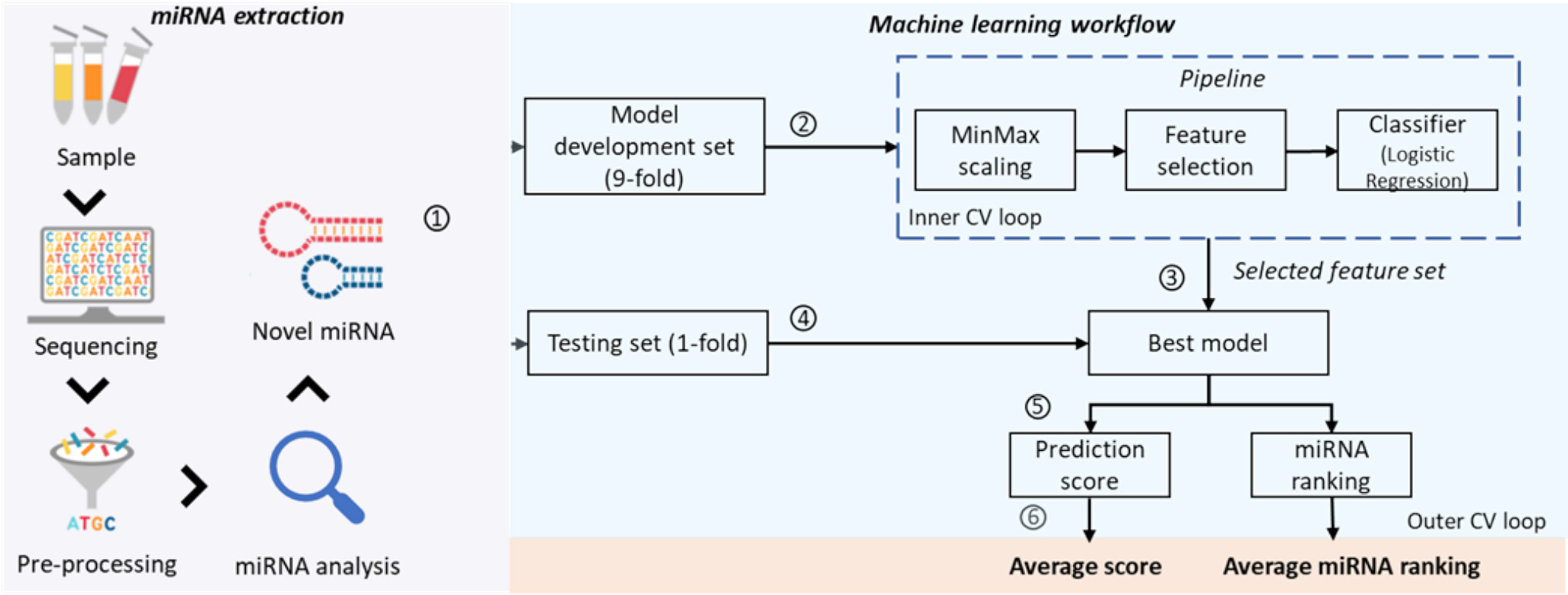
Major depressive disorder (MDD) is notably underdiagnosed and undertreated due to its complex nature and subjective diagnostic methods. Biomarker identification would help provide a clearer understanding of MDD aetiology. Although machine learning (ML) has been implemented in previous studies to study the alteration of microRNA (miRNA) levels in MDD cases, clinical translation has not been feasible due to the lack of interpretability (i.e. too many miRNAs for consideration) and stability. This study applied logistic regression (LR) model to the blood miRNA expression profile to differentiate patients with MDD (n = 60) from healthy controls (HCs, n = 60). Embedded (L1-regularised logistic regression) feature selector was utilised to extract clinically relevant miRNAs, and optimized for clinical application. Patients with MDD could be differentiated from HCs with the area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUC) of 0.81 on testing data when all available miRNAs were considered (which served as a benchmark). Our LR model selected miRNAs up to 5 (known as LR-5 model) emerged as the best model because it achieved a moderate classification ability (AUC = 0.75), relatively high interpretability (feature number = 5) and stability (∅ (Z) = 0.55) compared to the benchmark. The top-ranking miRNAs identified by our model have demonstrated associations with MDD pathways involving cytokine signalling in the immune system, the reelin signalling pathway, programmed cell death and cellular responses to stress. The LR-5 model, which is optimised based on ML design factors, may lead to a robust and clinically usable MDD diagnostic tool.
Posted on: May 2024
Authored: Tang Tong Boon