Research Success Stories
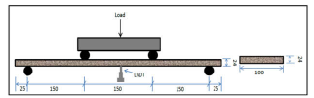
This paper presents the results of an experimental study that investigated the effects of two parameters: sand/fly ash (S/FA) ratio and water to geopolymer-solid (W/GS) ratio on the engineered geopolymer composite. The trial mix designs were optimized using the response surface method. These parameters influence the properties of the fresh and hardened geopolymer matrix, such as slump flow, compressive strength, flexural strength, elastic modulus, flexural toughness, ductility index and drying shrinkage. The optimizing process was conducted by developing statistical models using the response surface methodology (RSM) technique. The developed models were statistically validated and could be used to determine the desired response of engineered geopolymer composite (EGC) with a significance level of more than 95%. In this study, the optimized values of the S/FA ratio and W/GS ratio were obtained as 0.341701 and 0.225184, respectively. To validate the optimized S/FA ratio and W/GS ratio, an experimental study was performed, and a difference of less than 5% was found between predicted and experimental results.
Posted on: April 2020
Authored: Nasir Shafiq
In selecting the binder composition for oil well application, its stability is an important design parameter. This paper presents the results of an experimental study conducted for comparing the linear expansion characteristics of geopolymer cement with the traditionally used ASTM Class G cement system. The expansion test was done in a water bath at 60 Celcius subjected to different curing intervals. The linear expansion of a cement system defines as the dimensional changes occur in the system, which is sometimes required to avoid the cement shrinkage during the hydration phase. In the case when the desired level of expansion is not achieved in the system, then the commercially available expandable materials are added in the class G cement system that enables the system to expand to the desired level. Shrinkage in the cementing system causes the formation of a microannulus or induces a gap that may allow the migration of fluid, hence the integrity of the system could be lost. This experimental study has revealed that the geopolymer cement tends to expand 0.15%-0.2% without the addition of any admixture, whereas the ASTM Class G cement has shown a lower value of linear expansion, which was obtained less than 0.1% after 18 days of curing. In the case of Class G cement, the addition of expandable material helped to increase the expansion; in the case of a geopolymer system, the additive has further accelerated the expansion.
Posted on: February 2020
Authored: Nasir Shafiq