Research Success Stories
This study presents the influences of talc as an additive in intumescent coating formulations on the thermal insulation, degradation and water resistance. The fire test was performed according to ASTM-E119 standard to study the heat shielding properties of the coated substrates. The results showed that the 20% of the talc enhanced the heat shielding and recorded substrate temperature 75 °C after 100 min of fire test. The morphology of the char was analyzed by Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM). X-ray fluorescence (XRF), X-ray Diffraction (XRD) and Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR) results showed the presence of P2O5, MgO, TiO2, and SiO2 respectively. The functional groups analysis of char confirmed the presence of high temperature compounds and enhanced thermal performance of coatings. Thermogravimetric analysis (TGA) showed that addition of 20% talc increased residual mass of the char by 55.55%. The lap shear test result showed that the talc also improved the adhesion of the intumescent coating with steel substrate and the highest shear strength observed was 7 MPa for a formulation, F5 containing 20% talc. Water immersion test was performed according to ASTM D870-15 and the results showed the higher water-resistance was recorded for a formulation containing 10% talc in the control formulation.
Posted on: September 2017
Authored: Faiz Ahmad
Fire resistance of coatings mostly depends on the formation of char. In this work Multi-wall carbon nanotubes (MWCNTs) were used to improve fire retardant and char properties of the intumescent coating. Different coating formulations were prepared and their heat shielding performance was tested at 950 °C according to ASTM E-119. Char expansion was studied using fire furnace test. Field emission scanning electron microscope was used for char morphology. By means of X-ray Diffraction and Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy the presence of carbon, borophosphate; boron oxide and sassolite in the char was identified. Thermogravimetric analysis results showed that 0.5 wt%MWCNTs enhanced the residual weight of char up to 29.35 wt%. X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) confirmed that 0.5 wt% MWCNTs enhanced the carbon content up to 51.90 wt%, lowering oxygen content to approximately 25 wt% in the char that improved the fire resistance performance of the coating. Pyrolysis analysis confirmed that 0.5 wt% MWCNTs formulation released less gaseous products and reduced the decomposition of gaseous products. An accelerated weathering test ASTM D 6695-03 also revealed that 0.5 wt% of MWCNTs sustained its reliability up to 90 days in accelerated.
Posted on: March 2017
Authored: Faiz Ahmad
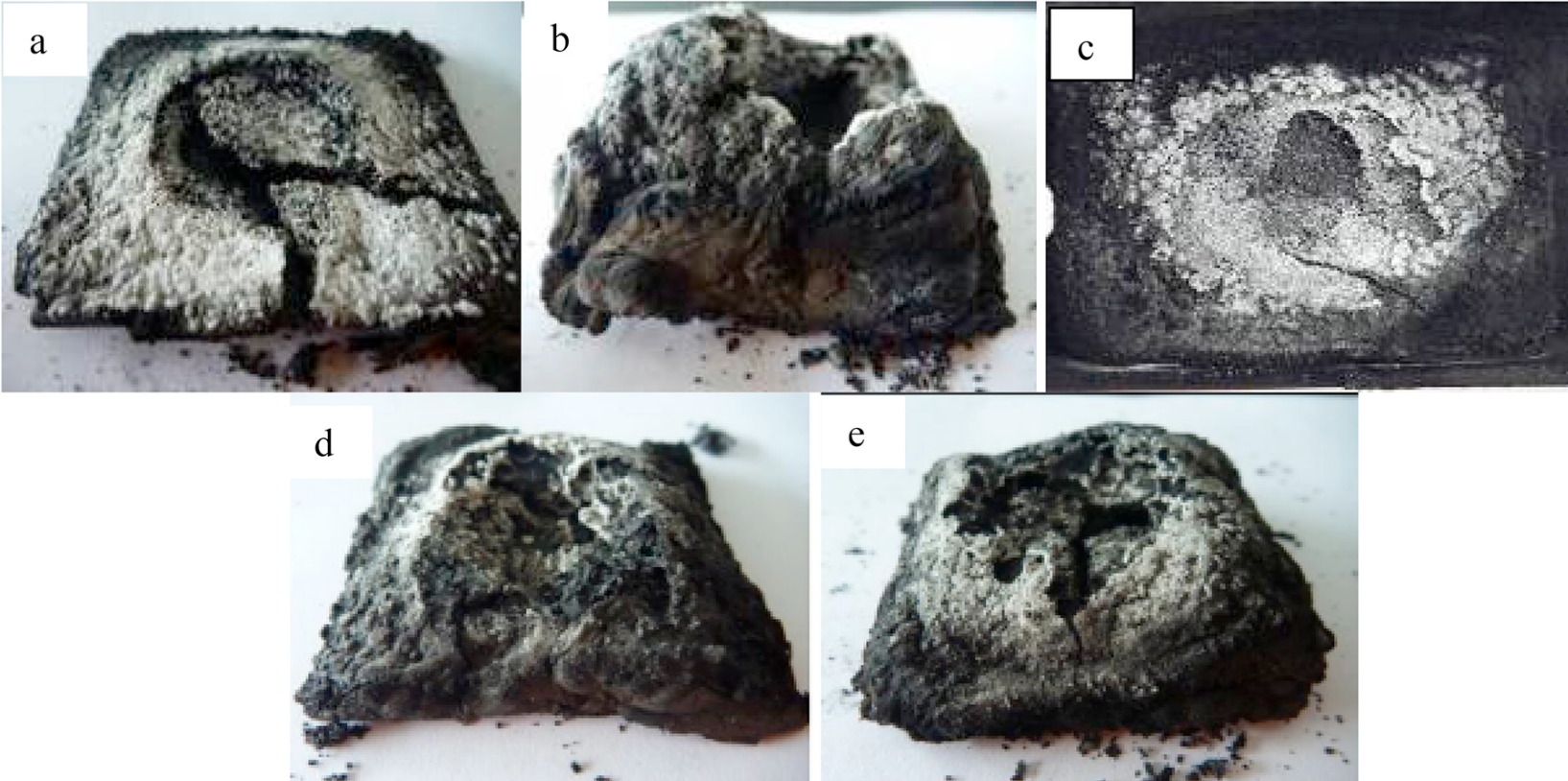
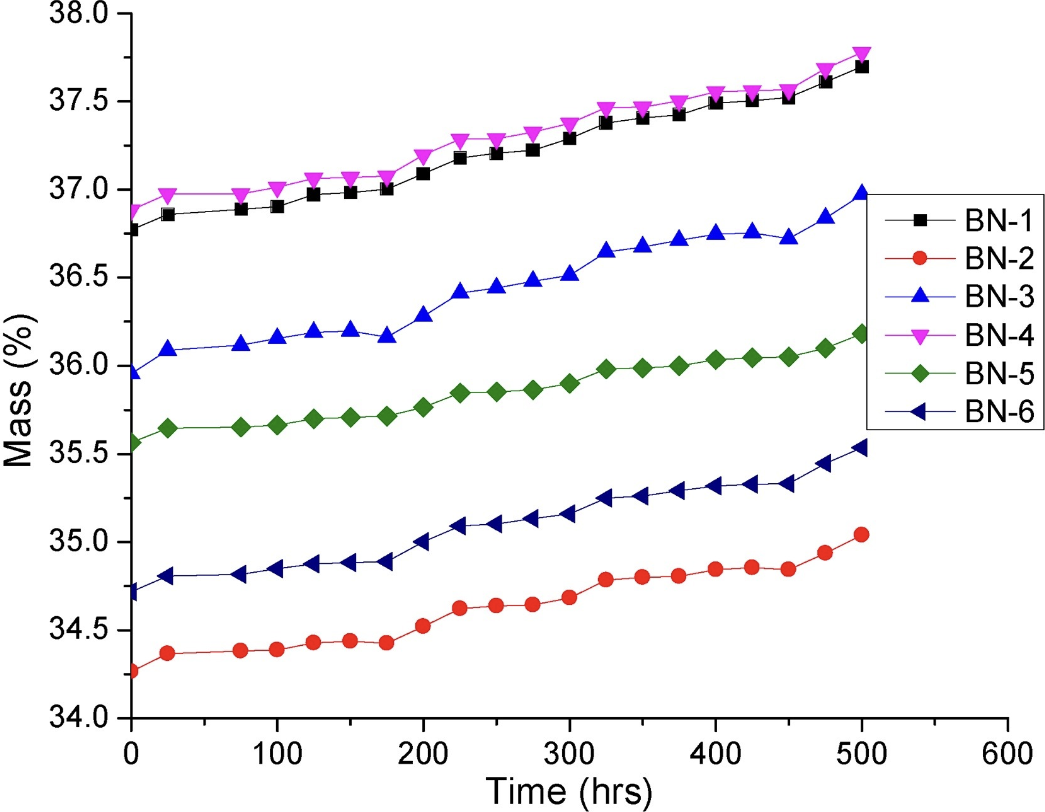
In present research work, the effect of nano-sized boron nitride (BN) was studied on intumescent fire retardant coating (IFRC) for structural application. The coated steel substrates were subjected to furnace fire test at 800 °C for 2 h and fire protection test for 1 h. The coatings were characterized by Thermogravimetric analysis (TGA) while the char from fire test was characterized by field emission scanning electron microscopy (FESEM), X-ray diffraction (XRD), Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR) and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS). Furnace fire test showed that IFRC reinforced with 4 mass% of nano-sized BN expanded more than 54.84% compared to the BN-1 formulation. Fire protection test performed for 1 h showed minimum substrate temperature of 140 °C with 4 mass% of BN which proved that the IFRC can successfully protect steel substrates within its critical temperature. A maximum of 44.49% residual mass was also recorded for the same coating. XRD analysis revealed that the remaining char contained boron phosphate, boron nitride and phosphoric nitride which are stable at high temperature. The presence of these compounds was also confirmed by functional group analysis using FTIR. FESEM confirmed that micrograph of char contained hexagonal BN. XPS analysis showed a fraction decrease in carbon contents of char residues of intumescent coating formulations with the increase of BN quantity. Pyrolysis GC-MS confirmed that formulations BN-4 released less gaseous product concentration compared to BN-1. Water immersion test showed that there was no trend of mass gain percentage with increasing amount of nano-sized boron nitride incorporated into the coating. The mass gain remained between 1.74% to 2.82%. Overall concluded that the formulation with 4 mass% BN effectively promoted the amount of char acted as a passive protective layer to the substrate resulting in lower substrate temperature with higher coating residual mass.
Posted on: June 2018
Authored:Faiz Ahmad
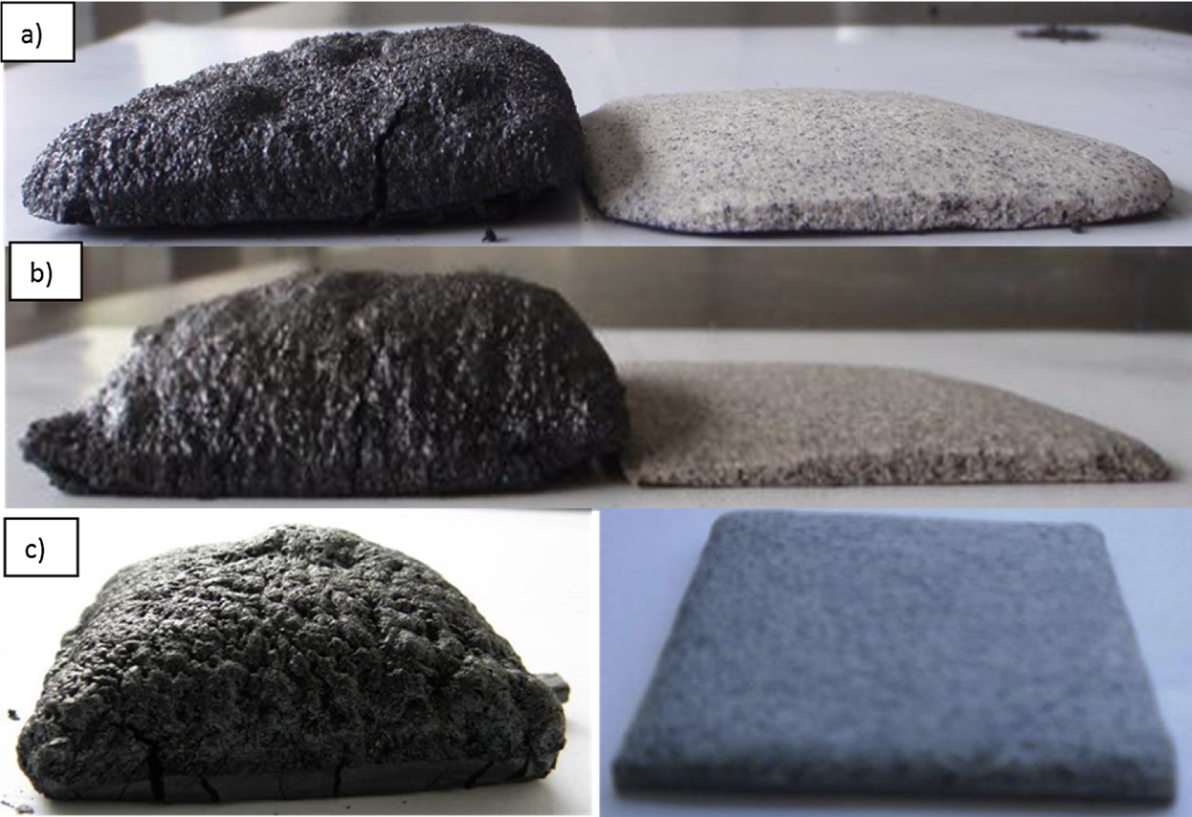
An intumescent coating is an insulating system designed to decrease the heat transfer a substrate structure. The intumescent fire retardant (IFR) coating presented here is based on expandable graphite (EG), ammonium polyphosphate (APP), melamine, and boric acid. Bisphenol epoxy resin BE-188 (BPA) was used as a binder with ACR Hardener H-2310 polyamide amine. Different formulations were developed to study the effects of APP and boric acid on char expansion, heat shielding, char morphology and char composition after a fire test. The coating was tested at 950°C for one hour. Char expansion was examined by furnace using a fire test. The results show that the coating is stable on the substrate. The morphology of the char was studied using Field Emission Scanning Electron Microscope (FESEM) of the coating after a fire test. X-ray Diffraction (XRD) and Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) showed the presence of carbon, borophosphate; boron oxide and sassolite in the residual char. Thermogravimetric analysis (TGA) including derivative plots showed that boric acid and APP enhance the residual weight of intumescent fire retardant coating. X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) confirmed that IF5 recorded better carbon content up to 47.45 wt%, in the residual char that enhanced the fire resistance performance of the coating. An accelerated weathering test according to ASTM D 6695-03 showed that the IF5 coating continued its reliability up to 90 days in the hastened weathering chamber.
Posted on: August 2017
Authored: Faiz Ahmad
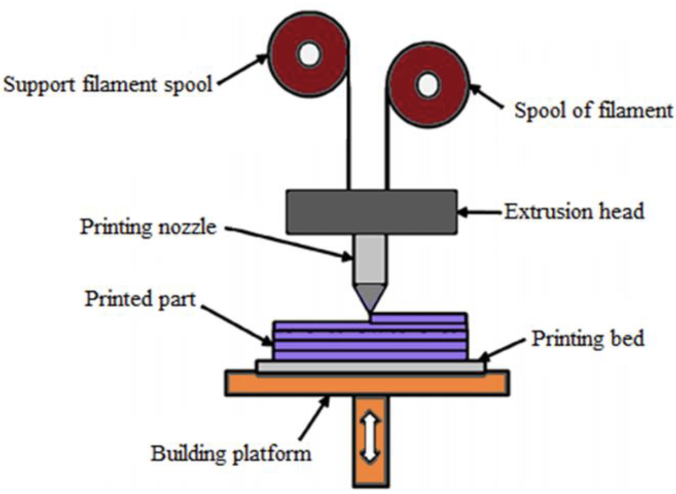
Additive manufacturing (AM) highlights developing complex and efficient parts for various uses. Fused deposition modelling (FDM) is the most frequent fabrication procedure used to make polymer products. Although it is widely used, due to its low characteristics, such as weak mechanical properties and poor surface, the types of polymer material that may be produced are limited, affecting the structural applications of FDM. Therefore, the FDM process utilises the polymer composition to produce a better physical product. The review's objective is to systematically document all critical information on FDMed-polymer composite processing, specifically for part fabrication. The review covers the published works on the FDMed-polymer composite from 2011 to 2021 based on our systematic literature review of more than 150 high-impact related research articles. The base and filler material used, and the process parameters including layer height, nozzle temperature, bed temperature, and screw type are also discussed in this review. FDM is utilised in various biomedical, automotive, and other manufacturing industries. This study is expected to be one of the essential pit-stops for future related works in the FDMed-polymeric composite study.
Posted on: December 2022
Authored: Faiz Ahmad