Research Success Stories
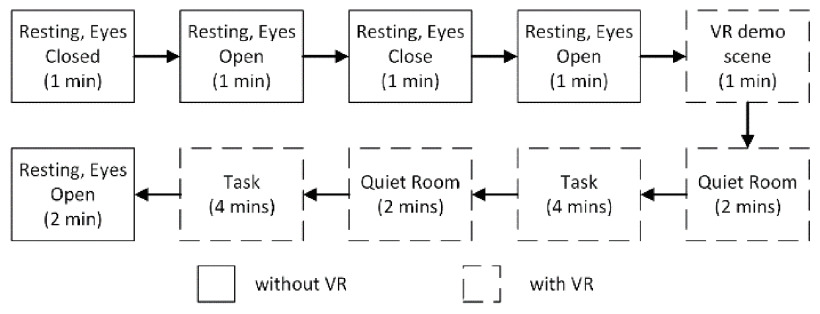
Resilience intervention is used to train and improve one's resilience level, however current studies used various psychometric instruments for resilience evaluation that are subjective, tedious, and prone to bias. In this study, electroencephalogram (EEG) has been chosen as a potential candidate for a new resilience assessment method that aims to rectify the limitations of existing psychometric instruments. The aim of the work is to create a practical resilience assessment system using EEG, which can classify low or high resilience level with high accuracy and generalization. The proposed system uses Virtual Reality headset to simulate rest and task conditions during EEG data acquisition. Connor-Davidson Resilience Scale (CD-RISC) is used to determine the actual resilience score of each participant. Results indicate that Linear Discriminant Analysis (LDA), Naïve Bayes (NB), and Support Vector Machine (SVM) using ReliefF for feature selection yields the best model performances, however other feature extraction and selection methods need to be explored to improve predictive strength of features on resilience. © 2024 IEEE.
Posted on: March 2024
Authored: Tang Tong Boon
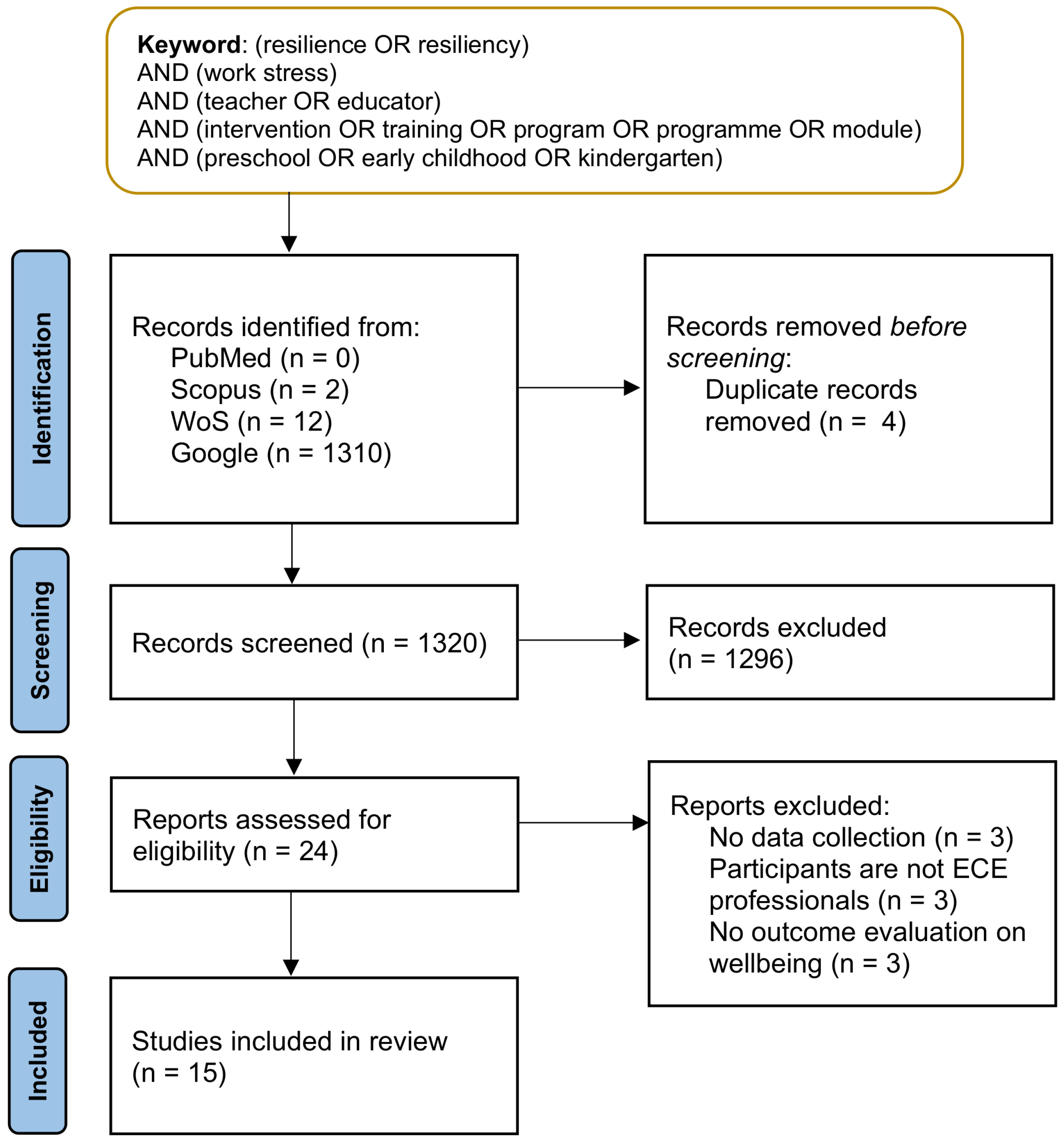
Resilience is a key factor that reflects a teacher's ability to utilize their emotional resources and working skills to provide high-quality teaching to children. Resilience-building interventions aim to promote positive psychological functioning and well-being. However, there is lack of evidence on whether these interventions improve the well-being or mental health of teachers in early childhood education (ECE) settings. This review examined the overall effectiveness of resilience-building interventions conducted on teachers working in the ECE field. A systematic approach is used to identify relevant studies that focus on resilience-building in countering work stress among early childhood educators. Findings from this review observed a preference of group approaches and varying durations of interventions. This review highlights the challenges of the group approach which can lead to lengthy interventions and attrition amongst participants. In addition to the concerns regarding response bias from self-report questionnaires, there is also a lack of physiological measures used to evaluate effects on mental health. The large efforts by 11 studies to integrate multiple centres into their intervention and the centre-based assessment performed by four studies highlight the need for a centre-focused approach to build resilience among teachers from various ECE centres. A pilot study is conducted to evaluate the feasibility of an integrated electroencephalography-virtual reality (EEG-VR) approach in building resilience in teachers, where the frontal brain activity can be monitored during a virtual classroom task. Overall, the findings of this review propose the integration of physiological measures to monitor changes in mental health throughout the resilience-building intervention and the use of VR as a tool to design a unique virtual environment.
Posted on: April 2022
Authored: Tang Tong Boon
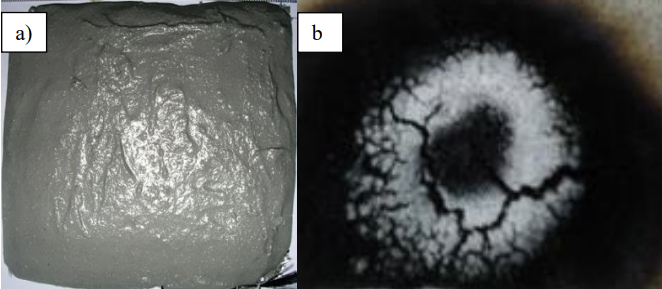
The aim of this work is to study corrosion behaviour of intumescent coating and the primer on steel substrate before and after a fire test. The coated steel substrates were subjected to fire in a furnace at 950oC for a variable duration ranging from 30, 45, 90 and 120 min. All coated steel substrates were also subjected to corrosion test by immersing them in 5% NaCl solution, for 15 min and three months duration using Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy (EIS). The specimen's impedance before fire test and before immersion was 4.37x108O.cm2. After 15 min exposure to NaCl, this value was reduced by 26, 53, 60 and 65% for specimens fired for 30, 45, 90 and 120 min, respectively. Further reduction in the impedance by 97.6, 97.8, 97.9 and 98.9% for samples fired for 30, 45, 90 and 120 min, respectively, were measured after three months in 5% NaCl immersion.
Posted on:September 2018
Authored: Faiz Ahmad
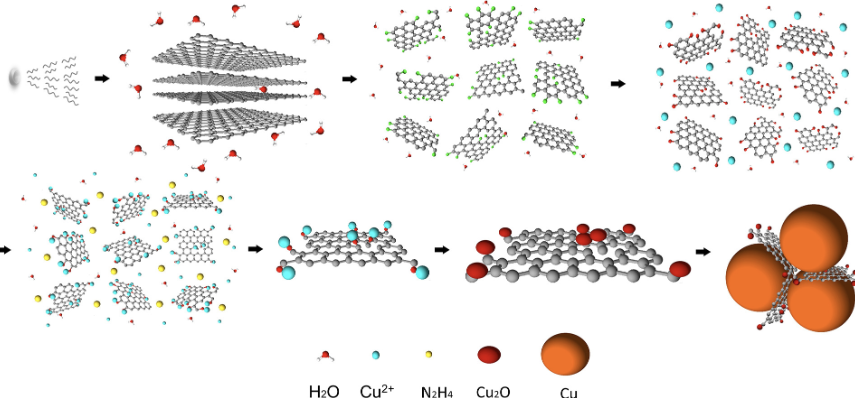
The challenges associated with inhomogeneous distribution, poor interfacial interaction, and agglomeration of graphene sheets in sintered metal composites restrict its effectiveness in improving mechanical and physical properties. This study devised a grafting protocol for attachment of metal oxides on graphene nanoplatelets (GNPs) to investigate its effect on dispersion and interaction with Cu matrix. GNPs were sonicated to enhance its functionalization without a considerable change in defect ratio followed by grafting of Cu2O nanoparticles on GNPs employing a co-precipitation protocol. XPS, Raman spectroscopy, XRD, FTIR, FESEM confirmed the successful growth of homogenously distributed Cu2O nanoparticles on GNPs. Subsequently, the interaction of Cu2O grafted GNPs with copper matrix was explored using powder injection molding (PIM). Microstructural analysis showed restricted agglomeration, improved distribution of GNPs in copper matrix, and most importantly, bridged interaction between bulk copper and graphene in sintered samples. Furthermore, the densification can still be improved by optimizing the sintering process.
Posted on:January 2022
Authored: Faiz Ahmad
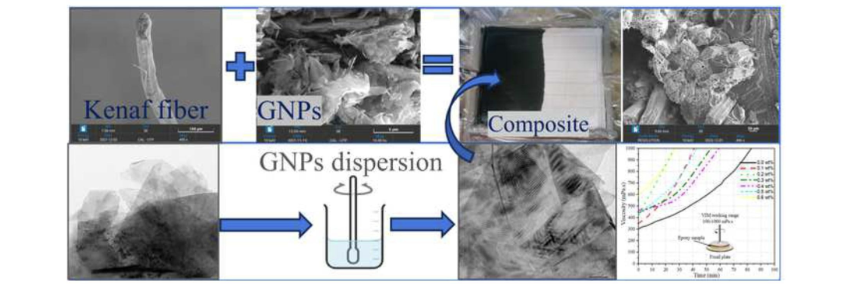
Kenaf composites have a high strength-to-weight ratio, but weak fiber-matrix interface bonding limits their automotive use. To address this, a novel technique was developed to fabricate multiphase composites using graphene nanoplatelets (GNPs), kenaf fibers, and an epoxy matrix. The composites were made using vacuum infusion molding, with the GNPs exfoliated using a bath sonicator for uniform dispersion. The composites modified with 0.2 wt% GNP showed the most significant improvement in mechanical properties. Specifically, these composites exhibited a 30.5% increase in tensile strength, a 61.5% increase in tensile modulus, a 17.6% increase in flexural strength, a 22.7% increase in flexural modulus, a 35.1% increase in interlaminar shear strength, and a 17.1% increase in fracture toughness. Additionally, the water absorption resistance of the multiphase composites improved by up to 7%. These improvements were attributed to the uniform dispersion of GNPs and improved interlocking with the fiber surface. The developed composite has the potential for interior parts (such as dashboards, interior walls, and luggage compartments) in the automotive vehicle.
Posted on: February 2024
Authored: Faiz Ahmad