Research Success Stories
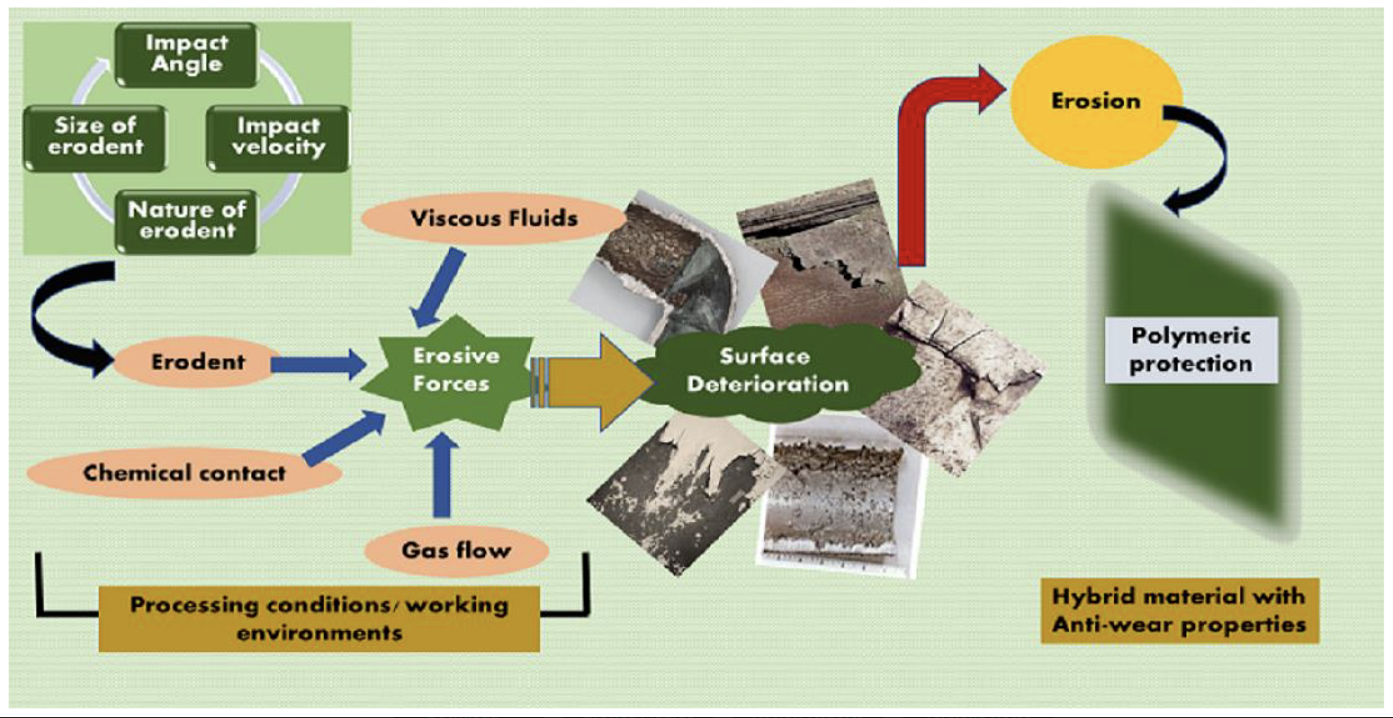
Erosion caused by the repeated impact of particles on the surface of a substance is a common wear method resulting in the gradual and continual loss of affected objects. It is a crucial problem in several modern industries because the surfaces of various products and materials are frequently subjected to destructively erosive situations. Polymers and their hybrid materials are suitable, in powdered form, for use as coatings in several different applications. This review paper aims to provide extensive information on the erosion behaviors of thermoset and thermoplastic neat resin and their hybrid material composites. Specific attention is paid to the influence of the properties of selected materials and to impingement parameters such as the incident angle of the erodent, the impact velocity of the erodent, the nature of the erodent, and the erosion mechanism. The review further extends the information available about the erosion techniques and numerical simulation methods used for wear studies of surfaces. An investigation was carried out to allow researchers to explore the available selection of materials and methods in terms of the conditions and parameters necessary to meet current and future needs and challenges, in technologically advanced industries, relating to the protection of surfaces. During the review, which was conducted on the findings in the literature of the past fifty years, it was noted that the thermoplastic nature of composites is a key component in determining their anti-wear properties; moreover, composites with lower glass transition, higher ductility, and greater crystallinity provide better protection against erosion in advanced surface applications.
Posted on: June 2022
Authored: Faiz Ahmad
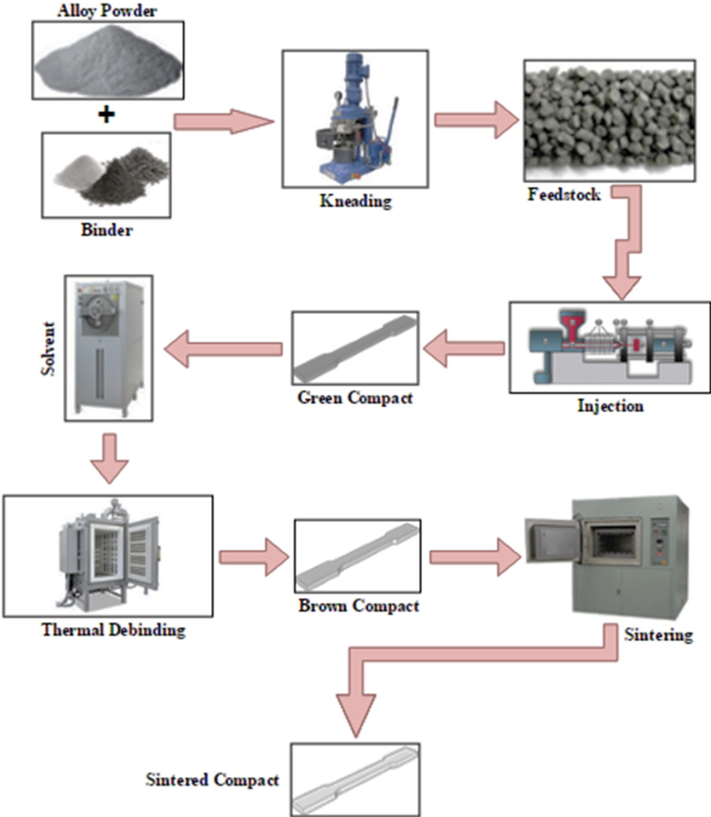
Biocompatible metals have been revolutionizing the biomedical field, predominantly in human implant applications, where these metals widely used as a substitute to or as function restoration of degenerated tissues or organs. Powder metallurgy techniques, in specific the metal injection moulding (MIM) process, have been employed for the fabrication of controlled porous structures used for dental and orthopaedic surgical implants. The porous metal implant allows bony tissue ingrowth on the implant surface, thereby enhancing fixation and recovery. This paper elaborates a systematic classification of various biocompatible metals from the aspect of MIM process as used in medical industries. In this study, three biocompatible metals are reviewed-stainless steels, cobalt alloys, and titanium alloys. The applications of MIM technology in biomedicine focusing primarily on the MIM process setting parameters discussed thoroughly. This paper should be of value to investigators who are interested in state of the art of metal powder metallurgy, particularly the MIM technology for biocompatible metal implant design and development.
Posted on: September 2017
Authored:Faiz Ahmad
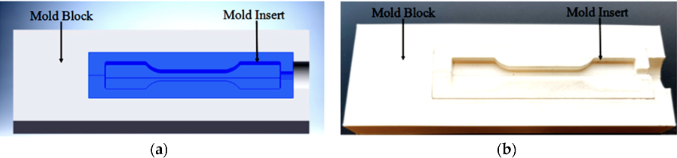
Conventionally, molds for metal injection molding (MIM) process are fabricated using metallic materials using conventional machining processes. Machined metal molds are resilient and therefore could be suitable for mass production of MIM parts. However, with the process of mass production leading to permanent hard tooling, the design is subjected to rigorous testing and iteration before finalization. During design analysis and the iteration process, the demand for MIM parts (part demand) is at low-volume. Therefore, machined metal molds could be costly and time consuming for low volume and customized end-use products. 3D printed molds could be a suitable choice for MIM production for such applications. The present study compares the performance of Fused Deposition Modelling (FDM) 3D printing (3DP) process made polymer molds with an aluminum mold for potential use in MIM process. It was observed that 3DP molds could successfully be used for a limited number of MIM cycles.
Posted on: June 2018
Authored:Faiz Ahmad
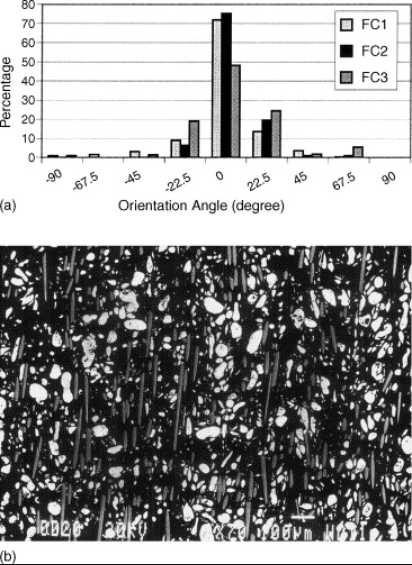
This research demonstrates the application of Multiple Live Feed Molding (MLFM) device for controlling the fiber orientations in powder injection molded aluminum composites. Experiments were performed for a range of powder/fibers composite mixes by using both Multiple Live Feed Molding device and molding technique. Optimum MLFM process parameters were identified to achieve the highest level of fiber orientation in aluminum composite test bars. Fiber orientation was measured in two planes of molded test bars. Average orientation angle "0" was determined and orientation factor "f" was calculated for composite moldings produced. This investigation has identified the molding composition to achieve the highest level of fiber orientations in a preferred direction, which should result in increased directional mechanical properties
Posted on: November 2005
Authored: Faiz Ahmad
The effects of zirconium silicate as a fire retardant reinforcement in the mixture of expandable graphite (EG), ammonium poly phosphate (APP), melamine, boric acid, bisphenol A epoxy resin BE-188(BPA) and ACR Hardener H-2310 polyamide amine are presented. Different formulations were developed to study the effects of zirconium silicate on char expansion, heat shielding, char morphology and composition after fire test. The coatings were tested at 950 °C using Bunsen burner for 1 h. The results show state that the zirconium silicate enhanced fire protection performance of intumescent coating. The morphology of the char was studied by Field emission scanning electron microscope (FESEM) after furnace fire test. X-ray Diffraction (XRD) and Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) results showed the presence of graphite, borophosphate; boron oxide and boric acid in the char. Thermogravimetric analysis (TGA) showed that zirconium silicate enhanced residual weight of char. X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) analysis showed that 5% zirconium silicate enhanced the carbon content up to 60.87% and lowered oxygen content to 28.09% in the residual char which proved helpful in improving the fire resistance performance of coating. Pyrolysis analysis confirmed that IF5-ZS releases less gaseous products concentration compared to IF-control coating.
Posted on: May 2014
Authored: Faiz Ahmad