Effects of ammonium polyphosphate and boric acid on the thermal degradation of an intumescent fire retardant coating
Author: Faiz Ahmad - August 2017
Sami Ullah, Azmi M. Shariff, Mohamad A. Bustam, Girma Gonfa, Qandeel. F. Gillani
Abstract
An intumescent coating is an insulating system designed to decrease the heat transfer a substrate structure. The intumescent fire retardant (IFR) coating presented here is based on expandable graphite (EG), ammonium polyphosphate (APP), melamine, and boric acid. Bisphenol epoxy resin BE-188 (BPA) was used as a binder with ACR Hardener H-2310 polyamide amine. Different formulations were developed to study the effects of APP and boric acid on char expansion, heat shielding, char morphology and char composition after a fire test. The coating was tested at 950°C for one hour. Char expansion was examined by furnace using a fire test. The results show that the coating is stable on the substrate. The morphology of the char was studied using Field Emission Scanning Electron Microscope (FESEM) of the coating after a fire test. X-ray Diffraction (XRD) and Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) showed the presence of carbon, borophosphate; boron oxide and sassolite in the residual char. Thermogravimetric analysis (TGA) including derivative plots showed that boric acid and APP enhance the residual weight of intumescent fire retardant coating. X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) confirmed that IF5 recorded better carbon content up to 47.45 wt%, in the residual char that enhanced the fire resistance performance of the coating. An accelerated weathering test according to ASTM D 6695-03 showed that the IF5 coating continued its reliability up to 90 days in the hastened weathering chamber.
Methodology
Flake graphite, melamine, and boric acid were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich (M) Sdn Bhd. Malaysia. Ammonium polyphosphate was provided by Clariant (Malaysia) Sdn Bhd. Acetic acid, sulphuric acid, KMnO4, bisphenol An epoxy resin BE-188 (BPA) and ACR Hardener H-2310 polyamide amine were bought from Mc-Growth chemical Sdn Bhd. Malaysia. Structural steel A36 M was supplied by TSA industries (Ipoh) Sdn. Bhd. Malaysia.
Impact & Benefits
Enhanced Fire Protection: Intumescent coatings are critical for protecting steel structures during fires by forming a carbonaceous char layer upon exposure to high temperatures. The incorporation of APP and boric acid further enhances this capability. They promote char formation and improve the residual weight of the char, which helps in reducing heat transfer to the substrate. This enhancement extends the structural integrity of steel, crucially maintaining it below collapse temperatures during fires.
Broad Application Potential: The use of APP and boric acid extends beyond steel structures. These additives are effective in various materials such as plastics, textiles, and coatings, enhancing their fire resistance. This versatility broadens the potential market for such fireproofing technologies across different industrial sectors where fire safety is paramount.
Technological Advancements: The research explores detailed effects on heat shielding, char expansion, morphology, composition, and thermal degradation of the coatings. Such advancements provide empirical evidence of performance improvements, which are crucial for gaining regulatory approvals and market acceptance.
Long-term Durability: Accelerated weathering tests demonstrate the durability of the enhanced coatings over extended periods (up to 90 days), indicating their reliability under various environmental conditions. This durability is essential for ensuring sustained fire protection over the lifespan of structures and materials.
Safety and Compliance: Meeting and exceeding fire safety standards and regulations is a primary benefit. By lowering substrate temperatures significantly during fires, these coatings enable safer evacuation times and better fire control measures, thereby enhancing overall building and occupant safety.
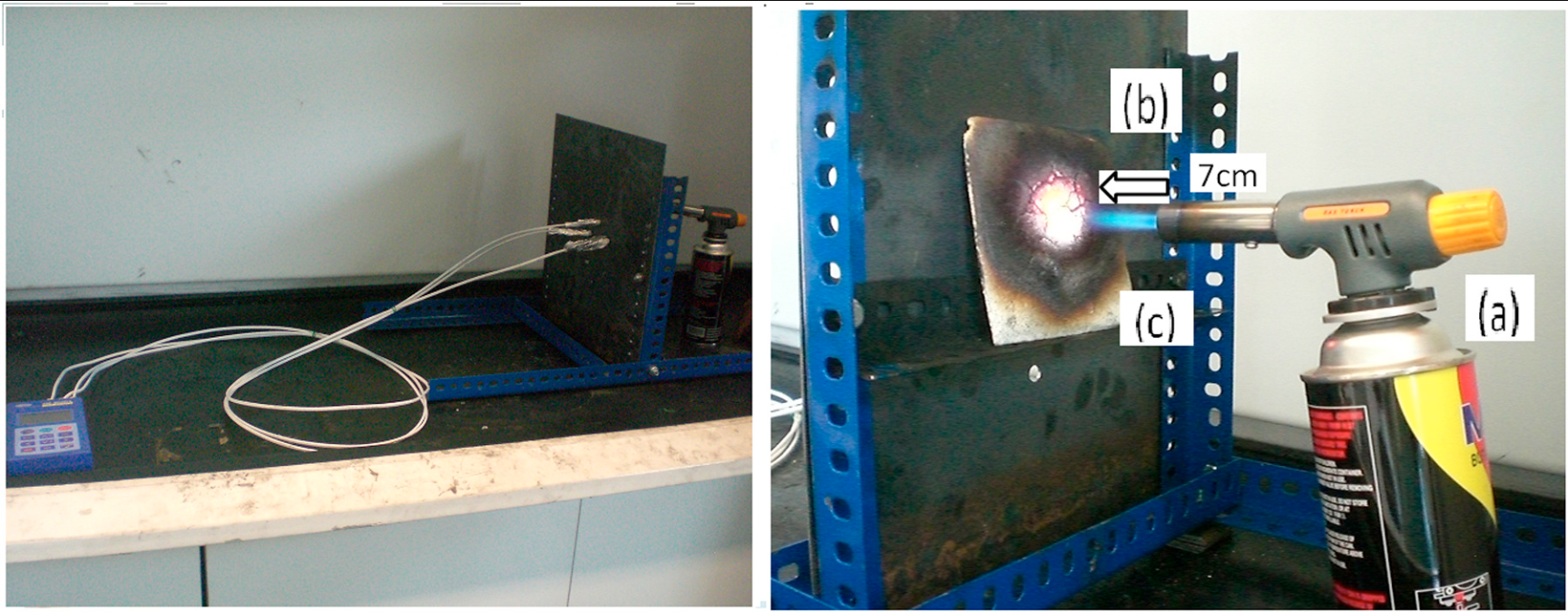
Findings/Figures and Research Data
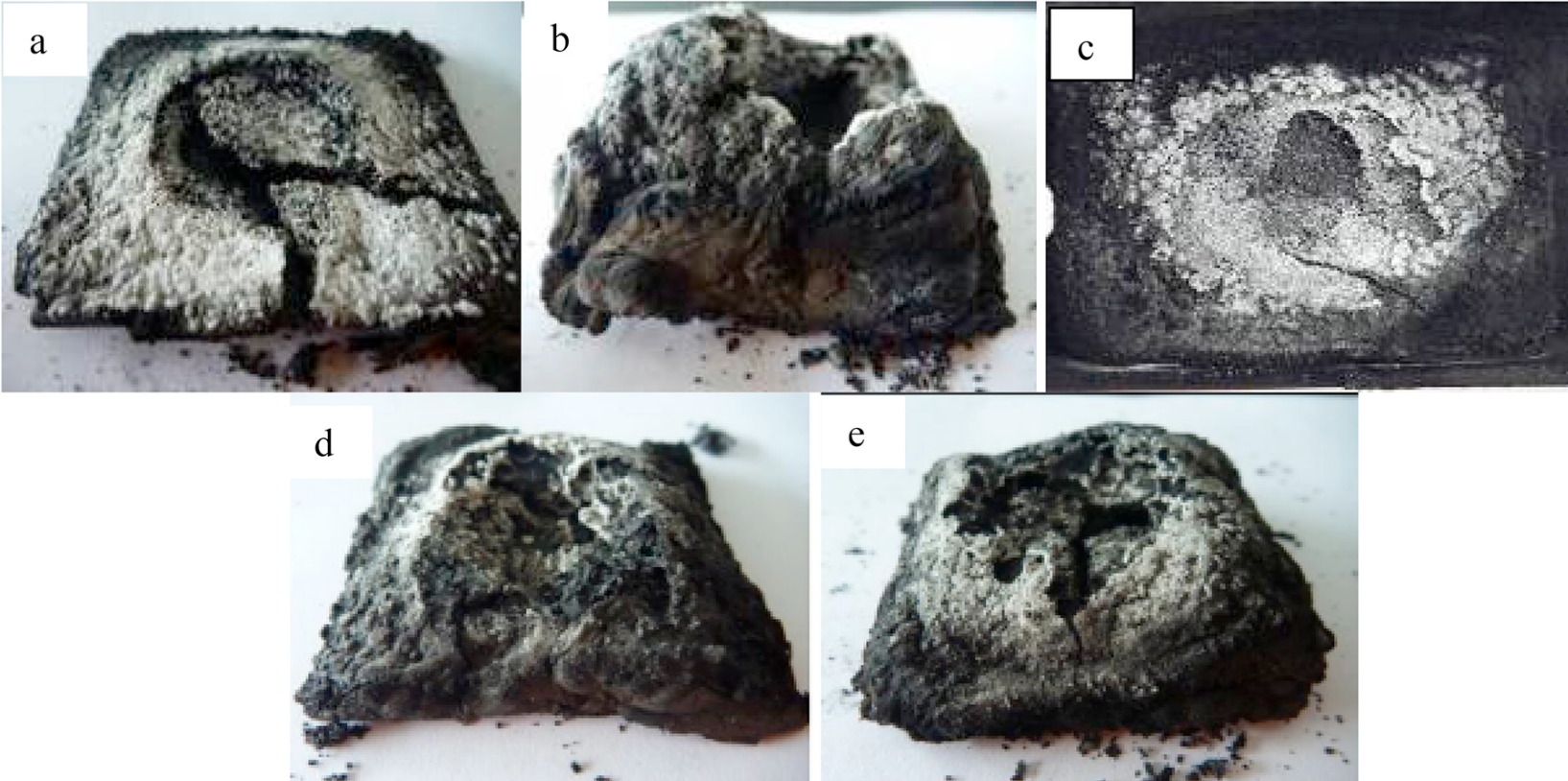
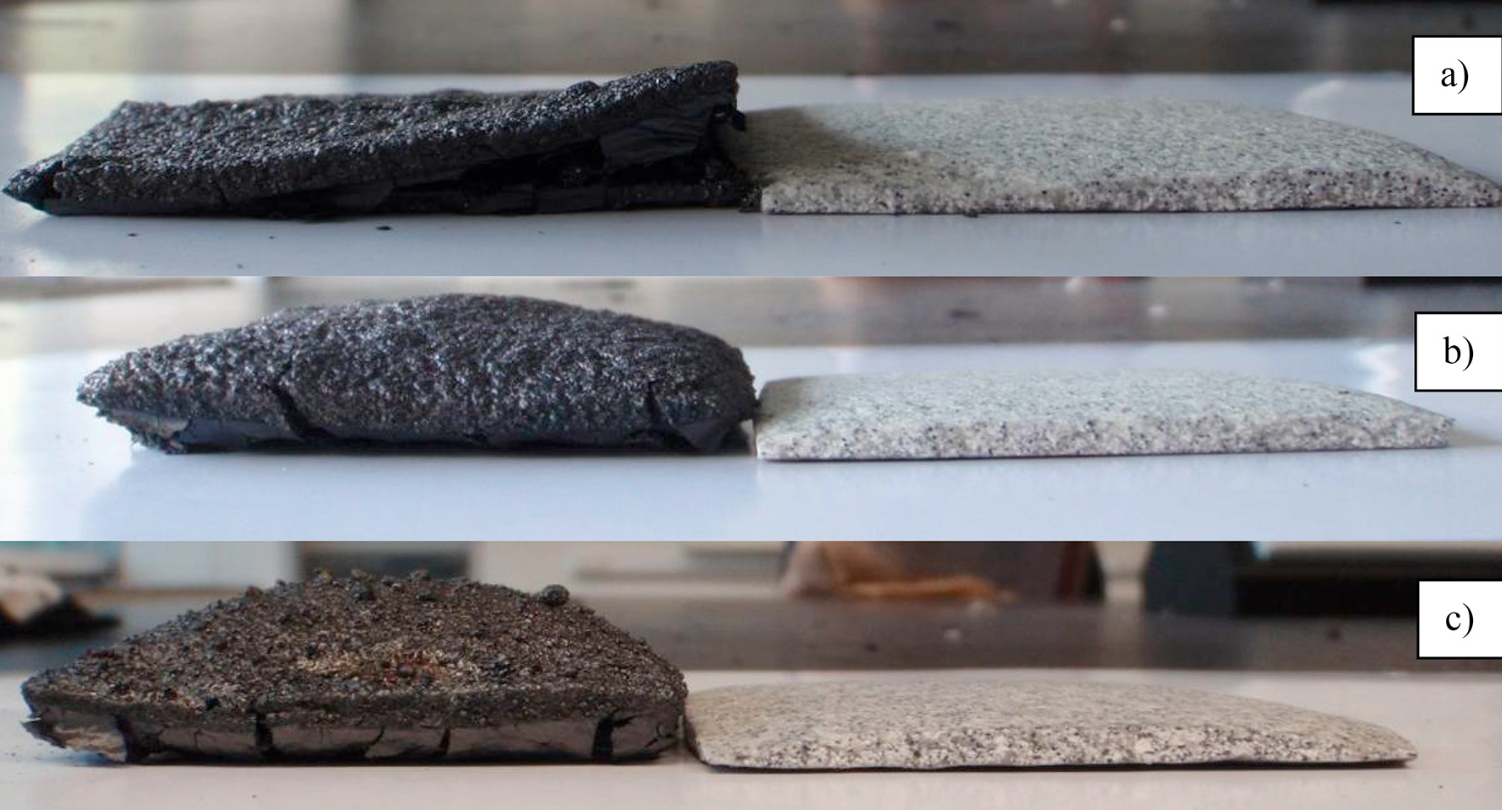
Time versus substrate temperature relationship for heat shielding/insulation is illustrated in Fig. 1, and the char expansion results are shown in Fig. 2. Five samples of coating with different compositions of intumescent ingredients were burnt at 950 °C; photographs of the resultant char are shown in Fig. 3. The char expansion results are as follows: 2 (IF1), 9.6 (IF2), 7.61 (IF3), 6.34 (IF4), and 5.27 (IF5) times, from their original coating thickness. The order of the char expansion is IF2 > IF3 > IF4 > IF5 > IF1. The formulation IF2 attained the high char expansion of 9.6 times from its original coating thickness due to the presence of APP (acid source, initiated the chemical reaction and formed a carbonaceous char) which expands the char [24]. Initially, the formulation expanded uniformly, but with the progressing fire over time, it was oxidized and could not protect the steel substrate.
Market Potential
Industry Demand:There is a consistent and growing demand for effective fire protection solutions, especially in construction and industrial sectors where steel structures need to maintain integrity during fires. Intumescent coatings are widely used for this purpose due to their ability to expand and form a protective char layer upon exposure to heat.
Technology and Innovation: The article discusses the use of APP and boric acid to enhance the fire retardant properties of intumescent coatings. This innovation addresses the need for more efficient and durable fire protection solutions that can withstand high temperatures and maintain structural integrity.
Material Advantages: Both APP and boric acid contribute unique properties to the coatings. APP promotes char formation and enhances the residual weight of the char, thereby improving heat shielding. Boric acid inhibits the release of combustible gases and contributes to char formation, further enhancing fire resistance
Market Size and Growth: The market for fireproofing materials is substantial and is expected to grow as safety regulations become stricter and awareness of fire hazards increases globally. Intumescent coatings, especially those incorporating advanced additives like APP and boric acid, are positioned to capture a significant share of this market due to their effectiveness and versatility.
Application Scope: The coatings described are applicable not only to steel structures but also to a variety of materials including plastics, textiles, and other industrial products that require fire protection. This broad application scope enhances their market potential across different industries.