Mass Transfer Performance Study for CO2 Absorption into Non-Precipitated Potassium Carbonate Promoted with Glycine Using Packed Absorption Column
Author: Azmi Shariff - May 2021
Nur Farhana Ajua Mustafa, Wee Horng Tay, Hairul Nazirah Abdul Halim, Siti Munirah Mhd Yusof
Abstract
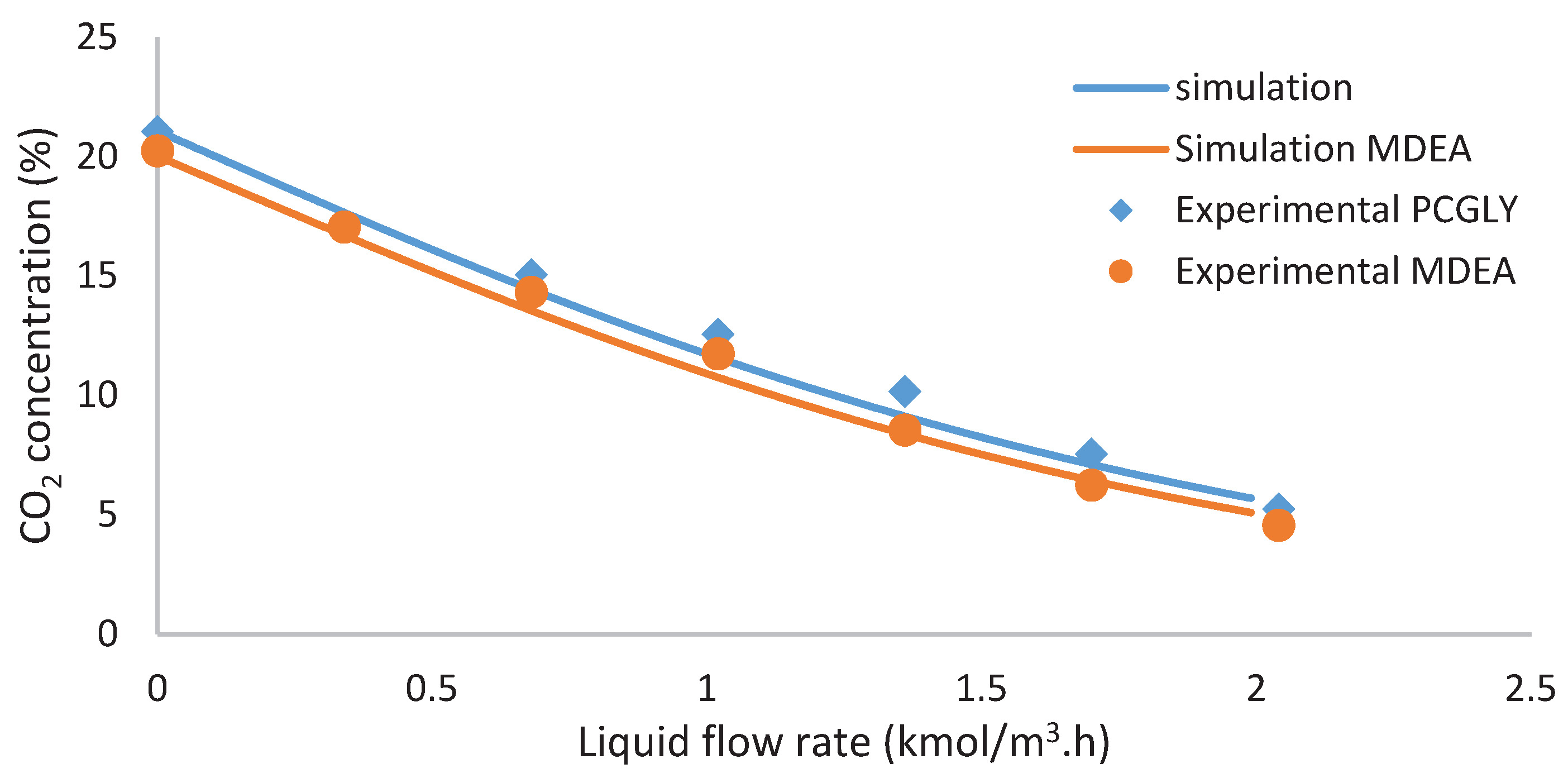
The removal of carbon dioxide (CO2) at offshore operation requires an absorption system with an environmentally friendly solvent that can operate at elevated pressure. Potassium carbonate promoted with glycine, PCGLY, is a green solvent that has potential for offshore applications. For high solvent concentrations at elevated pressure, the by-product of CO2 absorption consists of precipitates that increase operational difficulty. Therefore, this study was done to assess the CO2 absorption performance of non-precipitated PCGLY with concentration 15 wt% PC+3 wt% GLY, which is known to have comparable solubility performance with MDEA. A packed absorption column was used to identify the CO2 removal efficiency, mass transfer coefficient in liquid film, klae and overall volumetric mass transfer coefficient,KGav. A simplified rate-based model was used to determine klae and KGav based on the experimental data with a maximum MAE value, 0.057. The results showed that liquid flow rates and liquid temperature gives significant effects on the klae and KGav profile, whereas gas flow rate and operating pressure had little effect. The CO2 removal efficiency of PCGLY was found to be 77%, which was only 2% lower than 1.2 kmol/m3 MDEA. KGav of PCGLY is comparable with MDEA. The absorption process using PCGLY shows potential in the CO2 sweetening process at offshore.
Methodology
"In this study, the CO2 absorption performance of the PCGLY and MDEA were analysed using bench-scale packed absorption column. The column was packed with Sulzer metal gauze to increase the surface area and enhance the mass transfer. The mass transfer occurs through the direct contact between the gas mixture and solvent in a counter-current flow causes CO2 to be absorbed into the liquid phase. The CO2 concentration in the gas phase across the column by using an infrared (IR) analyser. The CO2 absorption performance of the solvents were evaluated by plotting the concentration profile against the column height at to determine the mass transfer coefficients (klae and KGav) by using a simplified numerical model. klae is a characteristic of the packing, which depends on the physical properties of the solvents such as viscosity, density, and surface tension. To observe the performance behavior of the solvent, klae was plotted over several process parameters such as liquid flow rate, gas flow rate, column pressure, and liquid inlet temperature without chemical enhancement. On the other hand, KGav, which is the overall mass transfer performance, was evaluated across the absorption column with chemical enhancement."
Impact & Benefits
Environmental Impact Reduction: The use of PCGLY as a solvent for CO2 removal offers an environmentally friendly alternative compared to traditional methods, contributing to reduced carbon emissions and environmental impact in offshore operations.
Cost Saving: Identifying PCGLY as a viable solvent option with comparable solubility performance to MDEA suggests potential cost savings in offshore CO2 removal processes, as PCGLY may offer a more cost-effective solution.
Industry Adoption Potential: With PCGLY demonstrating comparable CO2 removal efficiency and mass transfer coefficients to MDEA, the study suggests a potential for widespread adoption of PCGLY in CO2 sweetening processes offshore, opening up new possibilities for the industry.
Findings/Figures and Research Data
Based on the study, the absorption performance of PCGLY was well proven to be comparable with equimolar MDEA in terms of its CO2 removal efficiency and KGav. The potential of PCGLY is supported by its environmental friendly properties and has less toxicity than MDEA. PCGLY also requires lower regeneration energy as compared to MDEA. Due to the high solvent temperature in the absorber, the required energy for stripping process is lower. Another advantage of PCGLY as compared to MDEA is it is thermally stable and has no thermal degradation. Moreover, PCGLY is cheaper than MDEA, hence it can save more operational costs as compared to MDEA. Due to this, PCGLY is one of the potential alternative green solvents in CO2 absorption technology. Future research may focus on the evaluation of the energy consumption and control system for absorption system.
Market Potential
Environmental Benefits: Improved CO2 absorption rates and solubility lead to better overall carbon capture efficiencies, contributing to global efforts to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and combat climate change.
Cost Savings: By enhancing the properties of potassium carbonate through the addition of glycine, it becomes possible to achieve similar or even superior CO2 capture performances compared to traditional amine-based systems without the drawbacks of volatilization and corrosiveness.
Patent Landscape: There is evidence suggesting that potassium carbonate and its derivatives attract attention as alternative CO2 absorbents, indicating interest among researchers and industries in exploring new avenues beyond conventional amine-based systems.