Development of erosion-corrosion mechanisms for the study of steel surface behavior in a sand slurry
Author: Shaharin Anwar Sulaiman - August 2017
Abstract
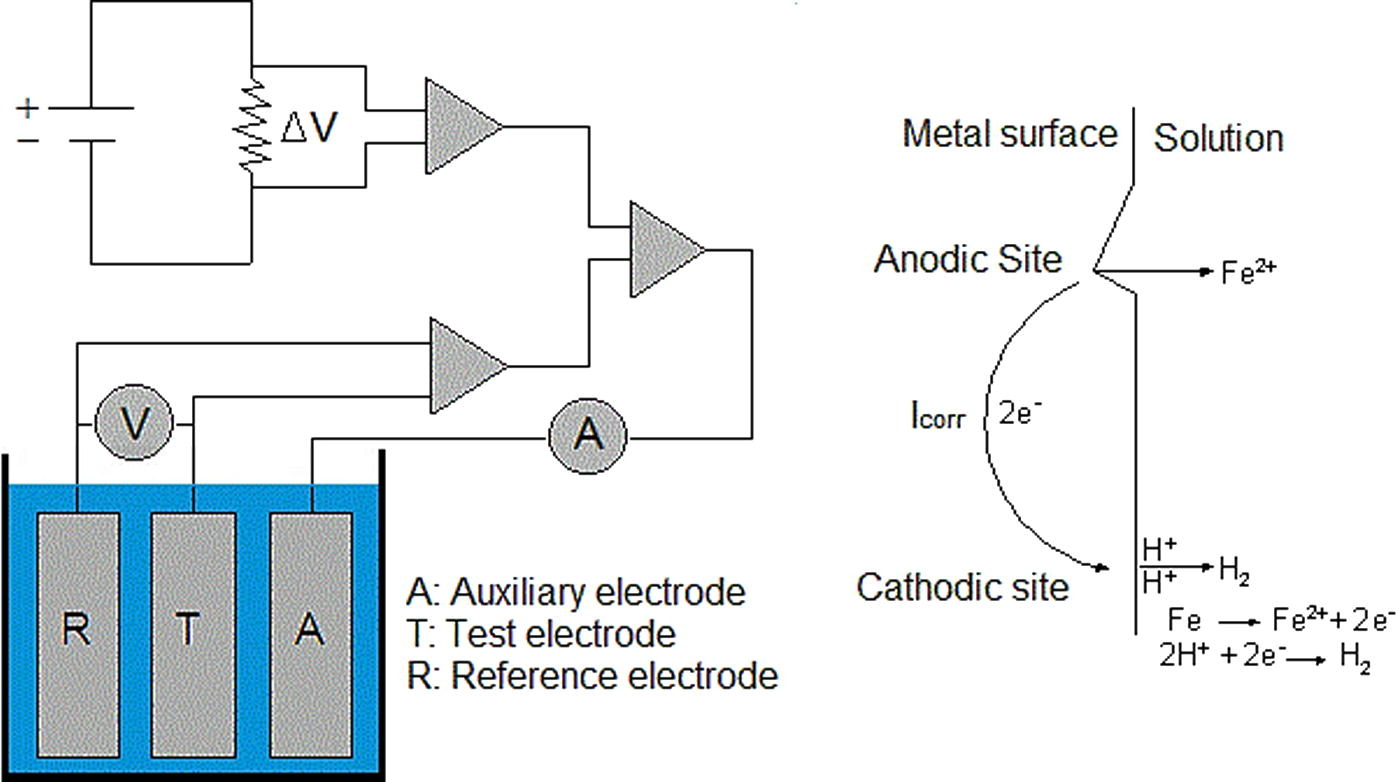
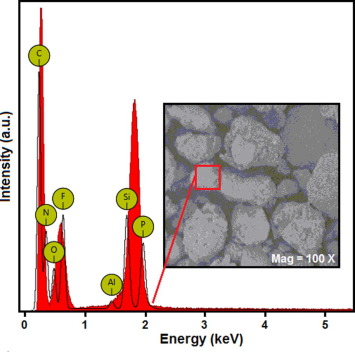
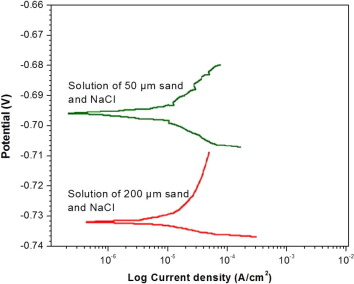
In this study, dry sand impact and linear polarization resistance (LPR) monitoring techniques were used to study the detrimental effects of the sand size on surface morphology of the mild steel. An electrochemical mechanism was developed to measure the resistance of the metal coupons rotating in a slurry of 4wt% NaCl and 5wt% sand. Scanning probe microscopy (SPM) and hardness testing of the eroded coupons were conducted to elaborate their surface topography. In-depth analysis revealed that not only the larger particles but smaller particles as well caused significant erosion-corrosion of the steel coupons. It was noticed that hardness and density of the erodent particles were reasonably high to induce the plastic deformation and micro-structures at the metal surface. The LPR measurements revealed high coupon resistance in the fine sand slurry than in the coarse sand slurry. The localized corrosion and erosion-corrosion attacks on the metal surface were also supplemented with the stirring rate and the presence of NaCl in the solution. The corrosion rate was sharply increased with an increase in stirring rate above 500rpm.
Methodology
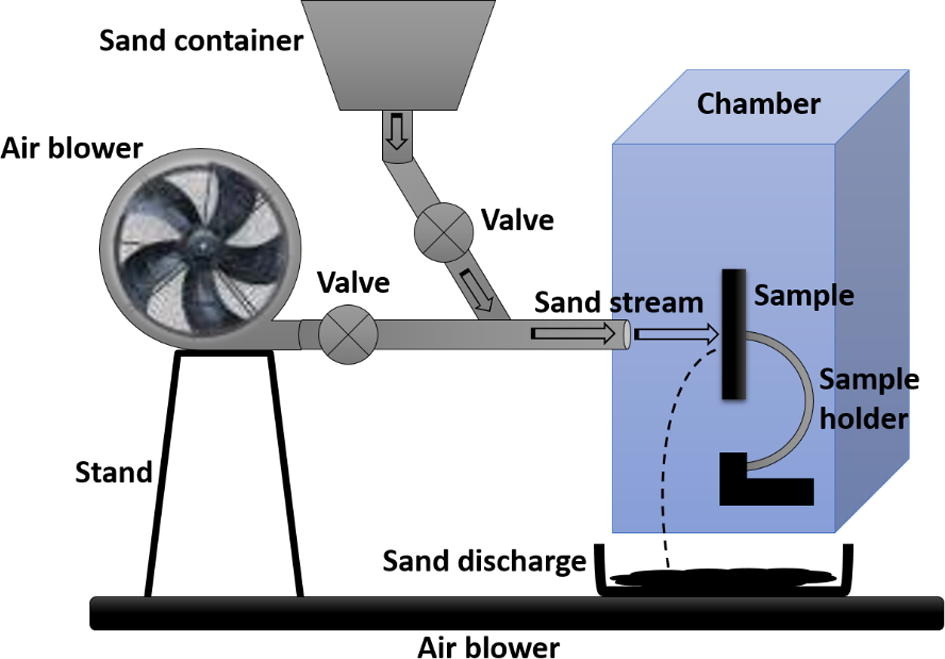
Experiments were conducted for the study of dry sand and electrochemical erosion-corrosion of the mild steel using 50 µm and 150 µm sand particles. The sand, used in these investigations, was a clastic sedimentary rock with particle size comparable to the fine sand. A dry sieving technique was employed to find the size distribution of the raw sand particles. The sand size classification analyses were carried out using a set of sieves of gradually reducing mesh size from 1.18 mm to 50 µm. The sand sample was placed on the top most screen in the series and seeped through all the screens from top to the bottom. Mechanical vibrations have also been used to help the grains of sand to permeate through the screen mesh. This technique was used to produce samples of coarse and fine sand with an average particle size of 50 µm and 200 µm, respectively.
Impact & Benefits
Improved understanding: It helps in gaining a deeper understanding of the complex interactions between abrasive particles, corrosive environments, and the steel surface. This understanding is crucial for developing effective strategies to mitigate erosion-corrosion damage.
Enhanced Material Selection: By studying erosion-corrosion behavior, researchers can identify materials that are more resistant to such processes. This information is valuable for industries where equipment is exposed to abrasive and corrosive environments, such as in mining, oil and gas, and chemical processing.
Optimized Equipement Design: Findings from erosion-corrosion studies can inform the design and engineering of equipment and structures that are exposed to abrasive slurries. This optimization can lead to longer equipment lifespan, reduced maintenance costs, and improved operational efficiency.
Risk Mitigation: Understanding erosion-corrosion mechanisms helps in assessing and mitigating risks associated with equipment failure and downtime. By implementing preventive measures based on this understanding, industries can minimize the likelihood of unexpected failures and associated financial losses.
Market Potential
Industry Demand: Industries such as oil and gas, mining, chemical processing, power generation, and water treatment rely heavily on equipment that operates in abrasive slurries. There is a growing demand for solutions that can mitigate erosion-corrosion damage and prolong the lifespan of equipment.
Regulatory Compliance: Regulatory bodies often impose stringent requirements on industries to minimize environmental impact and ensure worker safety. Compliance with these regulations drives the adoption of erosion-corrosion mitigation strategies, creating market demand for related technologies and services.
Cost Savings: Companies are constantly seeking ways to reduce operational costs and improve efficiency. Effective erosion-corrosion management can lead to significant cost savings by minimizing equipment downtime, maintenance expenses, and the need for premature equipment replacement.
Emerging Markets: With the expansion of industries in emerging economies, there is a growing market for erosion-corrosion mitigation solutions. As these industries modernize and adopt advanced technologies, the demand for effective erosion-corrosion mechanisms is expected to increase.