Bond Domain-Containing Octomer-Binding (NONO) protein expression and stability promotes the tumorigenicity and activation of Akt/MAPK/B-catenin pathways in human breast cancer cell Running title: NONO promotes the tumorigenicity of breast cancer
Author: Faiz Ahmad - November 2022
Abstract
Breast cancer is one of the most common cancers with high mortality, highlighting the vital need to identify new therapeutic targets. Here we report that Non-POU Domain-Containing Octamer-Binding (NONO) Protein is overexpressed in breast cancers and validated the interaction of WW domain of PIN1 with c-terminal Threonine-Proline (thr-pro) motifs of NONO. The interaction of NONO with PIN1 enhances NONO's stability by inhibiting its proteasomal degradation, and this identifies PIN1 as a positive regulator of NONO to promote breast tumor development. Functionally, silencing of NONO inhibits the growth, survival, migration and invasion, epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT), and stemness of breast cancer cells in vitro. A human metastatic breast cancer cell xenograft was established in transparent zebrafish (Danio rerio) embryos to study the metastasis inability of NONO silenced breast cancer cells in vivo. Biochemical analysis indicated NONO as a master regulator of the molecules associated with different hallmarks of cancer. Mechanistically, depletion of NONO promotes the expression of PDL1 cell surface protein in breast cancer cells. The identification of novel interactions of NONO with c-Jun and B-catenin proteins and activating the Akt/MAPK/B-catenin signalling suggests NONO as novel regulator of Akt/MAPK/B-catenin signalling pathways. Taken together, our results demonstrated an essential role of NONO in the tumorigenicity of breast cancer and could be a potential target for anti-cancerous drugs.
Methodology
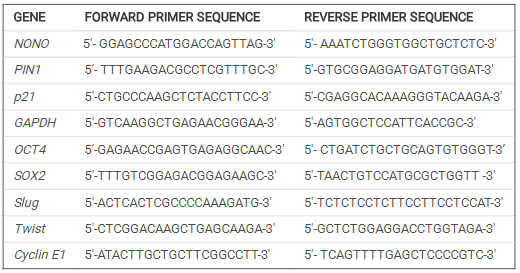
Crystal violet assay was used to determine the viability of NONO-depleted breast cancer cells. MDA-MB- 231 and MCF-7 cells were transfected with a scramble and NONO siRNAs in a six-well plate and incubated for 24 hours. The cells were then harvested and counted, and 5X103 cells were planted into each well of a 96-well plate and incubated at 37 Celcius, 5% CO2 for next 48 hours. After that, the medium was removed, and the cells were stained for 30 minutes with 0.4 percent crystal violet (prepared in 50 percent methanol). The wells were then cleansed with water to remove any remaining discoloration and air-dried for 12 hours. The next day, the dye was dissolved in 100 microliter of methanol, and the absorbance of the dissolved dye was measured at 570 nm. The viability of siRNA NONO w.r.t. siRNA scramble was determined as fold change absorbance value.
Impact & Benefits
Identification of Therapeutic Target: The significance of identifying new therapeutic targets for breast cancer, given its high mortality rate. The identification of Non-POU Domain-Containing Octamer-Binding (NONO) Protein as overexpressed in breast cancers suggests a potential target for therapeutic
Functional Implications of NONO Silencing:Silencing NONO is reported to have multiple functional implications in breast cancer cells, including the inhibition of growth, survival, migration, invasion, epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT), and stemness in vitro. This indicates that NONO plays a crucial role in various aspects of breast cancer cell behavior.
Target for Anti-Cancer Drugs:The results suggest that NONO could be a potential target for anti-cancerous drugs. This information opens up avenues for the development of targeted therapies aimed at inhibiting NONO's activity, potentially leading to more effective treatments for breast cancer.
Comprehensive Understanding: A comprehensive understanding of the molecular and functional aspects of NONO in breast cancer. This knowledge is crucial for designing targeted interventions and personalized treatment strategies.
Market Potential
Identification of NONO as a Tumor Promoter:The study focuses on the positive regulation of NONO by PIN1 and its contribution to tumor-promoting activity.
Inhibition of NONO and Therapeutic Potential:Inhibition of PIN1 reduces NONO levels in breast cancer cells.
Migration and Invasion Regulation:NONO knockdown leads to changes in the expression levels of migration-related proteins, including elevated E-cadherin and reduced MMP-2, MMP-9, and vimentin.
Cancer Stem Cell (CSC) Properties:NONO is implicated in the regulation of CSC-like properties, as evidenced by the reduction in CD24/CD44.