Composite amine mixed matrix membranes for high-pressure CO 2-CH 4 separation: synthesis, characterization and performance evaluation
Author: Hilmi Mukhtar - September 2020
Abstract
The key challenge in the synthesis of composite mixed matrix membrane (MMMs) is the incompatible membrane fabrication using porous support in the dry-wet phase inversion technique. The key objective of this research is to synthesize thin composite ternary (amine) mixed matrix membranes on microporous support by incorporating 10 wt% of carbon molecular sieve (CMS) and 5-15 wt% of diethanolamine (DEA) in polyethersulfone (PES) dope solution for the separation of carbon dioxide (CO2) from methane (CH4 ) at high-pressure applications. The developed membranes were evaluated for their morphological structure, thermal and mechanical stabilities, functional groups, as well as for CO 2 -CH4 separation performance at high pressure (10-30 bar). The results showed that the developed membranes have asymmetric structure, and they are mechanically strong at 30 bar. This new class of PES/CMS/ DEA composite MMMs exhibited improved gas permeance compared to pure PES composite polymeric membrane. CO2 - CH4 perm-selectivity enhanced from 8.15 to 16.04 at 15 wt% of DEA at 30 bar pressure. The performance of amine composite MMMs is theoretically predicted using a modified Maxwell model. The predictions were in good agreement with experimental data after applying the optimized values with AARE % = ~less than 2% and R2 = 0.99.
Methodology
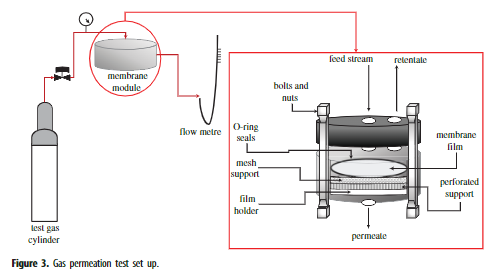
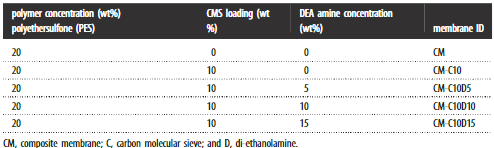
Five different types of membranes were synthesized in this study. The list of membranes synthesized, along with their concentrations, is tabulated in table 1. The polymer concentrations reported in this study were selected based on dope solution viscosity which has been studied in our previous study
Impact & Benefits
Superior Separation Performance for Industrial Applications: High-grade gas separation membranes for industrial applications should possess superior separation performance.
Desirable Membrane Characteristics:Membranes with these characteristics contribute to the reliability and longevity of industrial processes, ensuring cost-effectiveness and operational efficiency.
Incorporation of Inorganic Fillers in Mixed Matrix Membranes (MMMs):MMMs are reported to exhibit higher gas permeabilities and selectivities, providing enhanced gas separation performance compared to pure polymer membranes. This advancement can lead to more efficient and cost-effective
Market Potential
Enhanced CO2-CH4 Separation Performance: The asymmetric amine composite mixed matrix membranes (MMMs) demonstrated enhanced CO2-CH4 separation performance.
Twofold Increment in CO2 Permeance:The addition of diethanolamine (DEA) resulted in a more than twofold increment in CO2 permeance.
Threefold Increment in CO2-CH4 Selectivity:The asymmetric amine composite MMMs showed a threefold increment in CO2-CH4 selectivity compared to pure PES membrane.