Effects of Process Conditions on Calorific Value and Yield of Charcoal Produced from Pyrolysis of Coconut Shells
Author: Shaharin Anwar Sulaiman - April 2020
Abstract
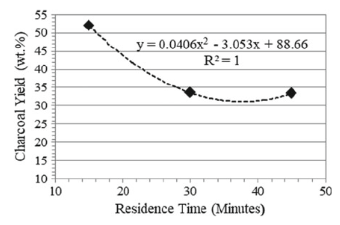
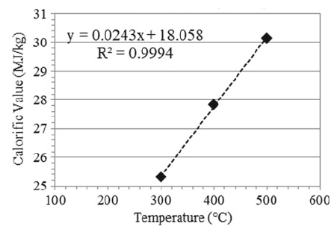
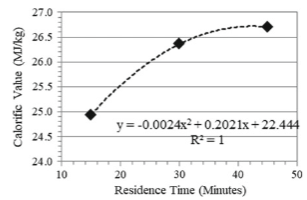
Charcoal, a black carbon residue, is mostly produced from the major conventional method where the biomass is allowed to be heated for several days in a kiln without studying the process condition. Most of the studies on the pyrolysis process focus on the liquid and gaseous by-products neglecting the solid to be used as a combustion fuel. For this study, charcoal was produced from coconut shells by the thermochemical conversion method of pyrolysis in a controlled nitrogen environment at temperatures of 300 Celcius, 400 Celcius, and 500 Celcius, and residence times of 15 min, 30 min, and 60 min. This was conducted to evaluate the process conditions' effects concerning the charcoal calorific value and yield. From the results obtained, a high process condition increases the calorific value, which results in a decrease in the charcoal yield. The lowest temperature gives a yield of 70.18 wt% and calorific value of 25.30 MJ/kg while the highest temperature produces a yield for as low as 26.57 wt% and a high calorific value of 30.15 MJ/kg. Furthermore, the charcoal yield tends to decrease from 51.99 to 33.10 wt% and the calorific value increases as the residence time increases from 15 to 45 min. Consequently, the thermal conversion undergone by the biomass may cause the changes of the quality parameters. Thus, charcoal can replace the use of fossil fuels because it presents energy content higher than that of lignite and similar to that of coal.
Methodology
The coconut shell was used as a feedstock and the tools include machete, oven,hammer, granulator, digital scale, bomb calorimeter, and pyrolysis reactor. Theprocess was carried out under different pyrolysis process conditions. The temperaturewas between 300 and 500 Celcius and residence time was between 15 and 45 min. Thesevalues were chosen as they were within the range of pyrolysis process condition assuggested by Basu
Impact & Benefits
Use of Biomass as a Primary Energy Source: Up to 80% of household energy requirements in developing countries are fulfilled by burning biomass such as wood, coal, and charcoal. This reliance on biomass has implications for resource usage, environmental impact, and potentially health concerns.
Characteristics of Traditional Charcoal Production:The downside of traditional charcoal production methods includes inefficiency, low yield, and adverse environmental effects.
Focus on Charcoal Production from Pyrolysis: The text emphasizes the potential application of pyrolysis for producing charcoal, which has various uses, including metallurgical and industrial fuel, purification, cooking, medicine, and as a carbon source. Compared to traditional biomass fuels, charcoal is described as cleaner, less smoky, and less smelly.
Utilization of Charcoal By-Products:While most studies focus on the liquid and gaseous by-products of pyrolysis, the text underscores the importance of the solid product (charcoal). Charcoal has a wide range of applications, making it a valuable by-product, and it is used for various purposes such as fuel, purification, cooking, medicine, and more.
Market Potential
Potential Replacement for Fossil Fuels: The text concludes that coconut shells, when processed through pyrolysis, can serve as a promising source of energy that can replace the use of fossil fuels. This aligns with the global trend toward seeking renewable and sustainable alternatives to traditional energy sources.
Application to Coconut Shells: The experimental study specifically focuses on coconut shells, suggesting that coconut shells can be carbonized effectively using pyrolysis. This implies a specific market niche for coconut shell charcoal, which could be marketed as a promising source of energy.
Confirmation from Previous Research:The observation regarding the inverse relationship between pyrolysis conditions, yield, and calorific value is noted to be consistent with findings from research on other materials like rapeseed, wood waste, and blackbutt. This lends credibility to the potential application of the pyrolysis method for various feedstocks.
Market Positioning:Companies or initiatives focusing on pyrolysis technology for charcoal production from coconut shells can position themselves as environmentally friendly, sustainable, and capable of catering to different market preferences (high yield or high energy content).