NitrogenPollution Impact and Remediation through Low Cost Starch Based Biodegradable polymers
Author: Shaharin Anwar Sulaiman - April 2020
Abstract
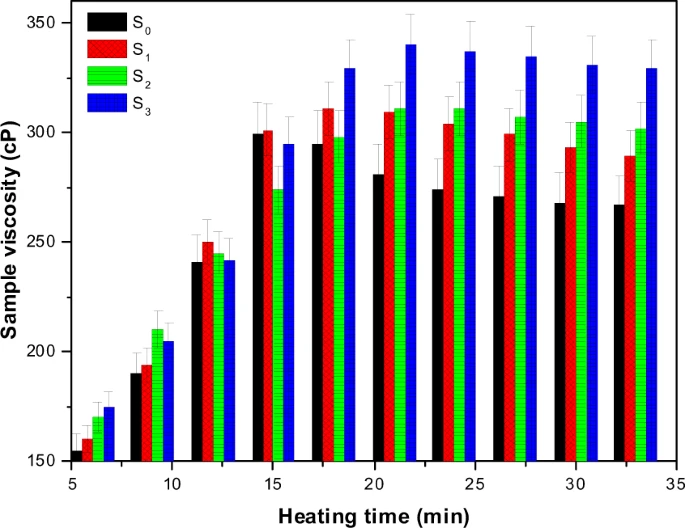
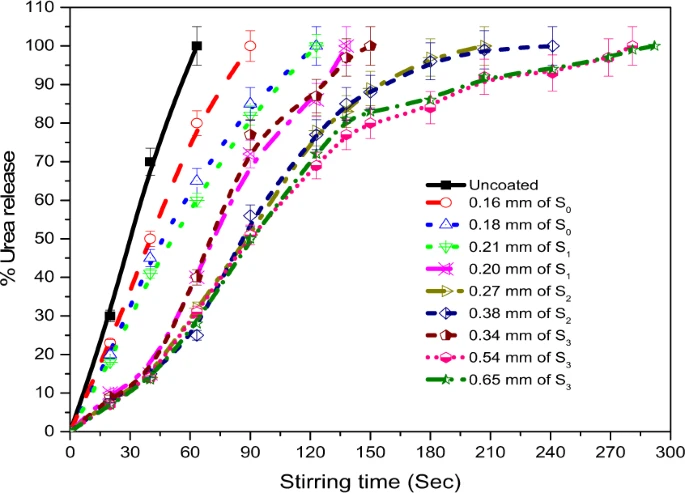
The world does not have too much time to ensure that the fast-growing population has enough land, food, water and energy. The rising food demand has brought a positive surge in fertilizers' demand and agriculture-based economy. The world is using 170 million tons of fertilizer every year for food, fuel, fiber, and feed. The nitrogenous fertilizers are being used to meet 48% of the total food demand of the world. High fertilizer inputs augment the reactive nitrogen levels in soil, air, and water. The unassimilated reactive nitrogen changes into a pollutant and harms the natural resources. The use of controlled-release fertilizers for slowing down the nutrients leaching has recently been practiced by farmers. However, to date, monitoring of the complete discharge time and discharge rate of controlled released fertilizers is not completely understood by the researchers. In this work, corn starch was thermally processed into a week gel-like coating material by reacting with urea and borate. The granular urea was coated with native and processed starch in a fluidized bed reactor having bottom-up fluid delivery system. The processed starch exhibited better thermal and mechanical stability as compared to the native starch. Unlike the pure starch, the storage modulus of the processed starch dominated the loss modulus. The release time of urea, coated with processed starch, remained remarkably larger than the uncoated urea.
Methodology
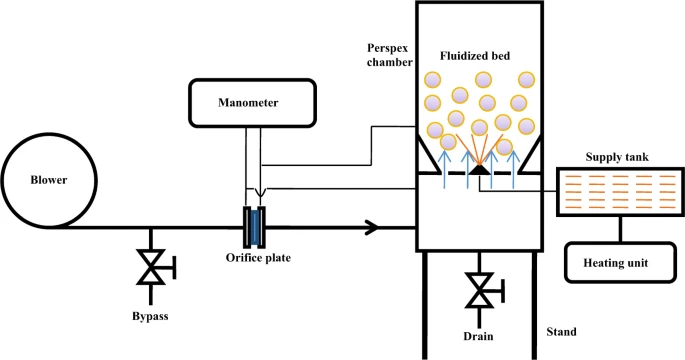
Both the uncoated and coated urea samples were inspected for coating thickness, percentage of coating mate-rial, coating morphology, nutrient discharge rate, complete dissolution time, and coating strength. Scanning elec-tron microscopy was used to elaborate the surface morphology and coating thickness of the coated urea. ?e crushing strength of the urea samples was measured with a tablet tester. The crushing strength was measured in terms of constant force (N). The force required to crack the coating is called coating sensitivity. A dissolution rate test was conducted to measure the discharge time of the uncoated and coated urea. In this test, the urea was released in distilled water under a shear rate of 200 rpm. Both coated?urea and control were weighed to 10 g and placed in separate glass beakers. A total of 200 mL of deionized water was added to the sample and the urea-water mixture was stirred at room temperature by using an overhead stirrer. The time for complete release of urea in distilled water was noted.
Impact & Benefits
Population Growth: The challenge posed by the fast-growing global population, indicating that there is limited time to address the increasing demand for essential resources such as land, food, water, and energy.
Innovation in Fertilizer Technology: An innovative approach - the use of controlled-release fertilizers. However, it points out that there is still a lack of complete understanding among researchers regarding the monitoring of the discharge time and rate of these fertilizers.
Environmental Protection: The development of controlled-release fertilizers and innovative coating materials aims to minimize the environmental impact of excess reactive nitrogen, potentially reducing pollution and harm to natural resources.
Technological Innovation: The research on coating material represents technological innovation in the field of agriculture and fertilizers, demonstrating a proactive approach to addressing challenges associated with fertilizer use.
Market Potential
Innovation in Controlled-Release Fertilizers:The development of a coated fertilizer with improved properties presents an innovative approach to addressing environmental concerns. If this technology proves effective and economically viable, it could attract interest from the agricultural sector.
Environmental Sustainability:With growing concerns about environmental sustainability, solutions that reduce the negative impact of agriculture, such as pollutant runoff from fertilizers, are likely to be well-received in the market.
Addressing a Global Challenge:A pressing global challenge of meeting the increasing demand for food while minimizing environmental impacts. Any solution that can contribute to sustainable agriculture practices has the potential for a significant market.
Potential Agricultural Adoption: If the coated urea with processed starch demonstrates a longer release time and better nutrient retention in the soil, farmers may be interested in adopting this technology to improve their crop yield and reduce environmental impact.