Effect of reaction time and microwave power on coil temperature duringmicrowave-metal interaction pyrolysis of plastics
Author: Shaharin Anwar Sulaiman - June 2020
Abstract
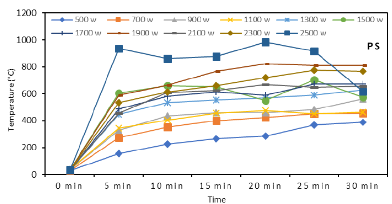
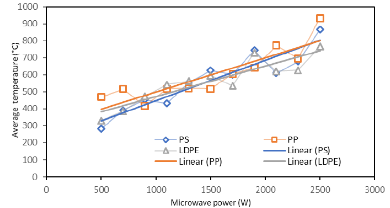
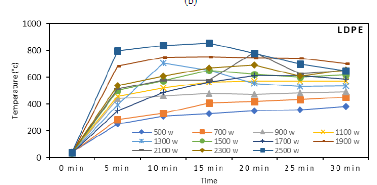
Rapid rise in production of plastic waste has posed a threat to environment due to its nonbiodegradable nature. In recent years, microwave assisted pyrolysis of plastic waste has emerged as a promising solution toward reduction of waste and recovery of value-added products and fuels. Previous works on microwave-metal interaction pyrolysis estimated only the peak value of coil temperature at a constant microwave power without monitoring complete reaction. The current study was directed toward investigating the effect of reaction time and variable microwave power on the coil temperature during microwave-metal interaction pyrolysis of plastics. The experiment was performed on individual plastics PS (polystyrene), PP (polypropylene) and LDPE (low density polyethylene) for comparative analysis. Pyrolysis was carried out for a reaction time of 30 minutes at different values of microwave power in the range of 500-2500 W. Type K thermocouple was used to monitor temperature of metal coil. Fluctuation in temperature of coil was found to be a consequence of interaction of coil and thermocouple with the microwaves. Maximum heating rate was observed in the first 5 minutes of microwave exposure. The slopes of average temperature versus microwave power were found to be nearly equal estimated as: PS = 0.24 Celcius/W, PP = 0.20 Celcius/W, LDPE = 0.18 Celcius/W, which indicated consistency in heating process for each plastic, achieved by the current set-up. Further, it was inferred that nature of plastic pyrolyzed had insignificant influence on coil temperature due to absence of direct contact between plastic and the coil.
Methodology
Heat generated through microwave-metal interaction using iron coil was used to pyrolyze the plastic samples. Temperature of coil was monitored for a total reaction time of 30 minutes at different values of microwave power in the range of 500-2500 W and for each plastic PS, PP and LDPE, selected for study. To investigate the consistency of heating process, average temperature attained by the coil during the entire reaction at constant microwave power was determined and plotted against the variable microwave power for each plastic.
Impact & Benefits
Impact
Environmental Issues:The environmental issues caused by the extensive use of plastic and the challenges associated with its disposal. Landfill and incineration are mentioned as problematic due to limited land availability, adverse environmental effects, and toxic emissions.
Increased Plastic Demand:The statistic presented indicates a steady increase in the demand for plastic over the years, contributing to the generation of significant amounts of plastic waste.
Toxic Emissions from Incineration: the environmental concerns associated with incineration, which produces toxic emissions harmful to life.
Benefits
Pyrolysis as an Alternative:microwave-assisted pyrolysis (MAP), as a viable alternative for plastic waste disposal. This method is presented as having the potential for energy recovery from waste.
Advantages of MAP: Microwave-assisted pyrolysis is portrayed as a promising option due to its benefits, including rapid and uniform heating over conventional methods. The mention of value-added chemicals and fuels produced through MAP demonstrates its potential for resource recovery.
Novel Technique: A novel technique in the form of microwave-metal interaction pyrolysis, using a metal coil as a reactor, is presented as an effective and competent alternative to previous methods.
Research Focus: The study's focus on investigating the effect of reaction time and variable microwave power on the coil temperature during microwave-metal interaction pyrolysis contributes to the understanding of the heating behavior in this process.
Market Potential
There is a growing market for sustainable waste disposal methods, considering the increasing environmental awareness and regulations.
The emphasis on the environmental drawbacks of current methods creates a potential market niche for cleaner alternatives.
Microwave-assisted pyrolysis, with its promising benefits, could attract attention from industries, municipalities, and environmental organizations looking for effective and eco-friendly waste disposal solutions.