Investigation of suitable graphene reinforcements for copper based PIM feedstock
Author: Faiz Ahmad - 2019
Abqaat Naseer, Faiz Ahmad, Ali Sameer Muhsan, Muhammad Aslam
Abstract
Graphene holds a remarkable potential as a reinforcement material for copper matrix due to its outstanding mechanical and electrical properties. However, noticeable increment in performance of graphene reinforced metal matrix composites is restricted due to inhomogeneous distribution and weak interfacial interaction between graphene reinforcement and metal matrix. Poor dispersion of graphene nanoplatelets can be attributed to absence of functional groups on graphene sheets, graphene oxide in contrast holds a large number of functional groups on its surface and edges, which make it dispersible in a wide range of matrices. In this research work, we investigate potential of graphene nanoplatelets and graphene oxide as reinforcement for copper based feedstock. During this study, two different approaches, solvent based mixing and copper grafting, have been employed as dispersion methods. A radical approach for incorporation of graphene in metal matrix is also devised, by taking benefit from functional nature of graphene oxide and anchoring copper particles on graphene oxide sheets. Successful growth of copper particles along with simultaneous reduction of graphene oxide have been observed by using scanning electron microscopy and infrared spectroscopy analysis. Copper particles as intercalation species present a viable potential to resist re-agglomeration of graphene sheets while enhancing the interfacial interaction between copper matrix and graphene at the same time. Copper graphene nanocomposite can potentially be used as a reinforcement for copper based powder injection molding feedstock.
Methodology
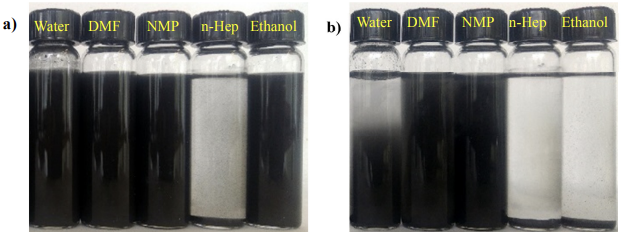
In order to evaluate the dispersion level of GNPs in different solvent initial batch of formulation were prepared with five different solvent NMP, DMF, Ethanol, n-Heptane and water at a concentration of 1.0 mg/ml. for uniform dispersion of GNPs in respective solvents, suspensions were sonicated for 2 h. On the base of their performance and solubility with PW three solvents, NMP, DMF and n-Heptane, were selected from initial batch for further processing. In the next step, selected solvents NMP, DMF and n-Heptane were mixed with paraffin wax with volumetric ratio of 1:1 and this mixture were used for further dispersion of GNPs at a concentration of 1.0 mg/ml. This processing was performed using magnetic stirring for 30 minutes at a temperature of 60 ° C. Developed samples were solidified at room temperature. A control sample was also prepared by adding GNPs in liquid paraffin wax at concentration of 1.0 mg/ml and using same procedure as mentioned above.
Impact & Benefits
Graphene Research: The article contributes to the growing body of knowledge on graphene, particularly its reinforcement in metal matrix composites, highlighting ongoing challenges and potential solutions.
Enhanced Material Properties: The findings can lead to the development of materials with superior strength, thermal, and electrical properties, which are crucial for high-performance applications in various industries.
Cost-Effective Production:The focus on cost-effective production methods like PIM could lower manufacturing costs, making advanced materials more affordable and promoting their widespread adoption.
Improved Composite Materials: The article provides insights into creating more efficient and effective graphene-reinforced metal composites, potentially leading to breakthroughs in various technological fields.
New Market Opportunities: Development of graphene-reinforced composites opens up new markets and applications, stimulating economic growth in sectors such as electronics, aerospace, automotive, and construction.
High-Performance Applications: Products incorporating graphene-reinforced composites will benefit from enhanced performance characteristics, such as increased durability, better thermal management, and improved electrical conductivity.
Findings/Figures and Research Data
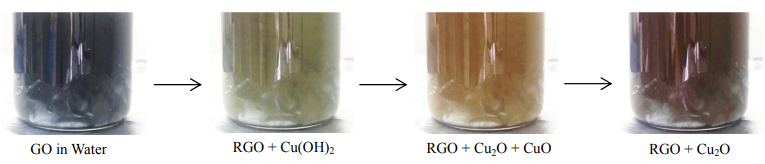
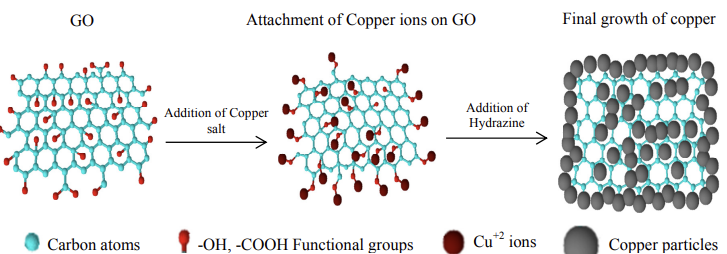
The original theme behind adaptation of this process is to take advantage of functional groups of GO for dispersion and exfoliation in water and then introducing copper ions in the solution to act as intercalation specie between graphene sheets. This will not only enhance the dispersion of graphene sheets but will also improve the interface between carbon atom and copper during feedstock preparation steps. Cu-RGO nanocomposite powder can be mixed with pure copper powder and binder system to prepare homogenously reinforced PIM feedstock. However, further characterization and optimization of process parameters is necessary to evaluate dispersion of CuRGO in PW and PIM binder system, before employing this method for PIM feedstock preparation.
Market Potential
Unique Properties of Graphene: The article mentions graphene's exceptional strength and thermal and electrical conductivity. These properties make it a valuable material for enhancing conventional materials, indicating significant demand in industries requiring high-performance materials, such as electronics, aerospace, and automotive.
Graphene Reinforced Composites: The article points out slower progress in graphene-reinforced metal matrix composites, particularly due to challenges in processing. This implies an untapped market potential, especially if these challenges can be overcome.
Research and Development Focus: The article discusses ongoing research to improve the dispersion and interface of graphene in metal matrices, particularly copper. This research focus indicates potential market growth as these issues are resolved.
Functionalization of Graphene:The article highlights the use of GO to improve solubility and interaction with metal matrices. This functionalization opens up further applications in various industries, expanding market potential.