Intumescent flame retardant coating based graphene oxide and halloysite nanotubes
Author: Faiz Ahmad -2021
Siti Maznah Kabeb, Azman Hassan, Zurina Mohamad, Zalilah Sharer
Abstract
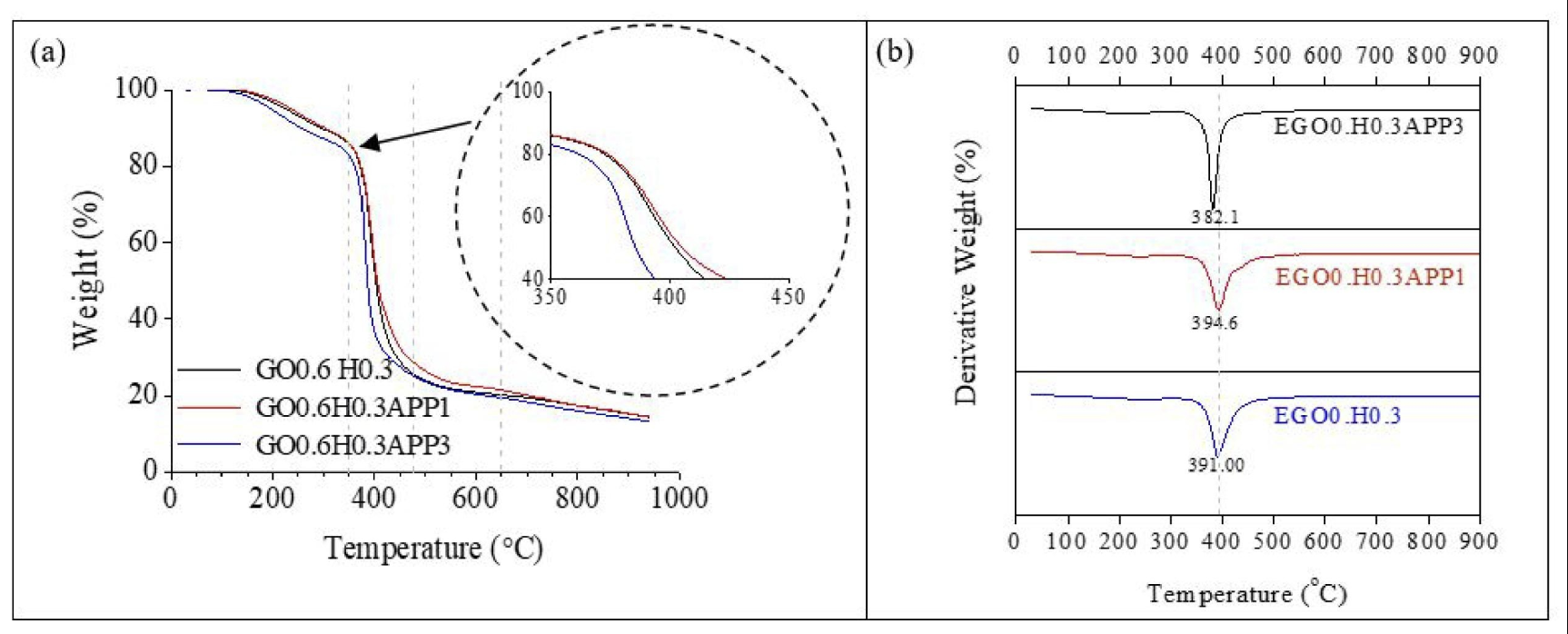
Epoxy nanocomposites coatings filled with hybrid graphene oxide/halloysites (GO/HNT) based intumescent flame-retardant additives (IFR) have been fabricated and investigated in terms of flame retardancy property, thermal stability, and adhesion strength. The dispersion and interaction of the nanofillers with the matrix were characterized by transmission electron microscopy (TEM) and Fourier transform infrared (FTIR). The synergistic flame-retardant effects of ammonium polyphosphate (APP) on flame retardancy properties and thermal stability were investigated by limiting oxygen index (LOI) and thermogravimetric analysis (TGA), respectively. The result shows that the epoxy coating with hybrid GO/HNT based IFR achieve an LOI of 26 % at 1 phr of APP (EGO0.6H0.3APP1). Meanwhile, the maximum mass loss of the EGO0.6H0.3APP1 coating sample is 391.0 ° which showing an increment by 1.3 % compared with neat epoxy coating, demonstrating excellent thermal stability performance. The char residue also suggests, APP played a synergistic flame-retardant mechanism with a combination of hybrid GO/HNT. The presence of hybrid GO/HNT/IFR considerably enhances adhesion strength between the coating material and metal substrate. The EGO0.6H0.3APP1 showed the maximum LOI value, thermal stability, and adhesion strength among the studied formulations.
Methodology
Diglycidyl ether of bisphenol A (DGEBA) epoxy resin (BE-188), polyamine hardener (H2310 polyamine amide) were purchased from by Mc-Growth Chem. Graphene Oxide (UGOXTM) was bought from United Nano Tech Innovations Pvt Ltd. Montmorillonite (Nanomer ® 1.44P) was obtained from Nanocor, United Stated. Ammonium polyphosphate (APP), Melamine (MEL), and pentaerythritol (PER) was purchased from Innovative Pultrusion Sdn. Bhd.
Impact & Benefits
Increased Load-Bearing Capacity: Structural steel loses its load-bearing capacity at high temperatures (500-600 °). IFR coatings can maintain structural integrity and load-bearing capacity for 1-3 hours at temperatures above 1100 °, providing crucial time for evacuation and fire-fighting efforts.
High Limiting Oxygen Index (LOI): The highest LOI value of 26.0 indicates that the material is highly resistant to ignition and combustion, thus enhancing overall fire safety.
Reduced Harmful Emissions: The absence of molten dripping and toxic fumes reduces the environmental impact during fire incidents.
Char Formation and Strength:The multi-cellular char formed by APP, PER, and MEL additives acts as a robust physical barrier, protecting the substrate from fire. The presence of MWCNTs enhances the char strength by sealing cracks and joining char layers.
Building Regulations:Meeting and exceeding building fire safety regulations across various countries and regions ensures compliance and enhances the safety of occupants.
Construction and Infrastructure:The construction industry, particularly in regions with stringent fire safety standards, is likely to adopt these advanced coatings widely, driving market growth.
Sustainable Building Materials: The shift towards halogen-free, low-toxicity flame retardants supports the development of sustainable building materials, aligning with global environmental goals.
Findings/Figures and Research Data
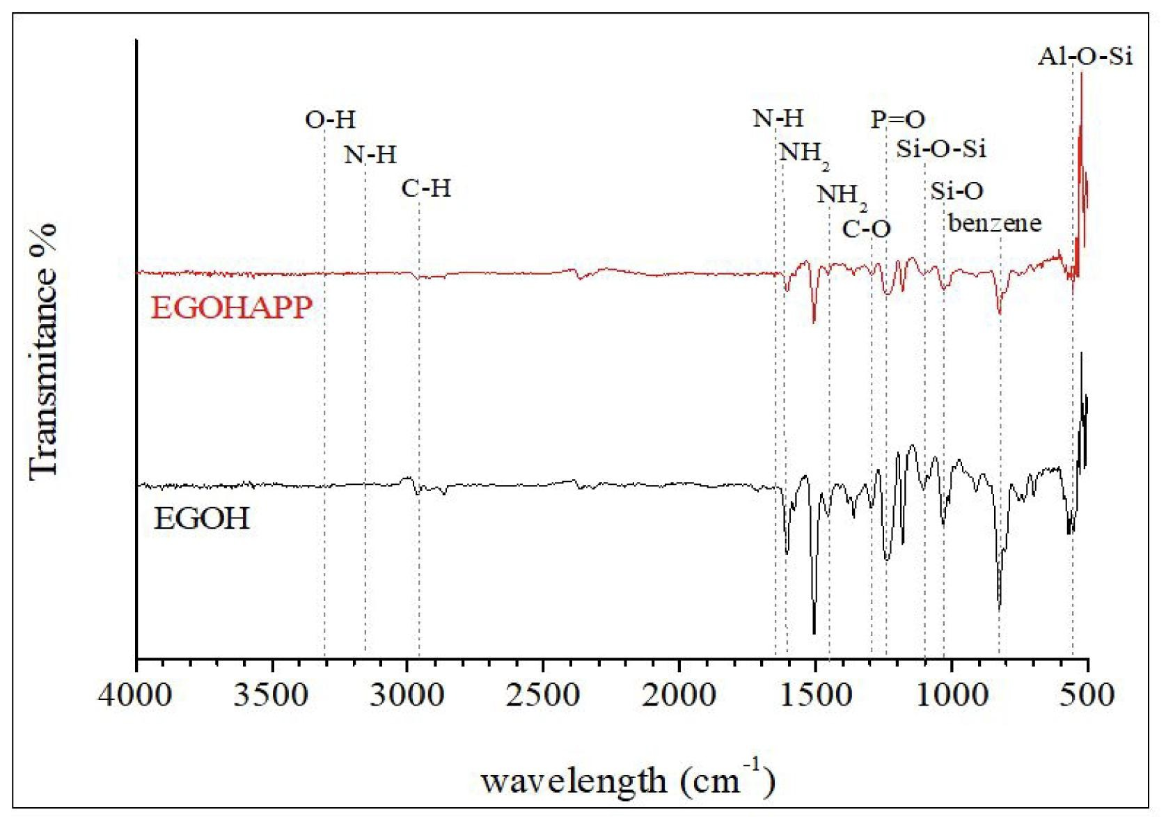
The TEM image in Fig. 3 demonstrated the actual structure of the hybrid GO/HNT based IFR coating after the second step of processing i.e. sonication and mechanical agitation technique. Results shows, the nanofillers, and IFR particles were randomly dispersed in an epoxy matrix with exfoliated/intercalated clay galleries as well as agglomerated nanoclay (indicates with the white arrow in Fig. 3) respectively [10]. The dark strips correspond to agglomerated stacking layers of silicates, while the thin grey lines indicate the exfoliation of clay platelets. Aggregation and agglomerations of the stack of clay are detectable in some areas of the TEM image implying the fact that a uniform dispersion is not achievable [26]. This observation is expected since the intrinsic hydrophilic nature of nanoclay and the strong van der Waals attraction forces between lamellae prohibited the relatively hydrophobic epoxy chains to penetrate the galleries of the layers and break the stacks down to the primary layer [26].
Market Potential
Fire Safety Regulations: Stringent fire safety regulations worldwide require buildings to incorporate fire-resistant materials to prevent structural collapse during fires. IFR coatings provide essential fire protection, maintaining structural integrity for a crucial period during a fire.
Environmental Concerns: Traditional flame retardants often contain halogens, which can produce toxic smoke and fumes. IFR coatings are halogen-free and offer advantages like low smoke, low toxicity, and low corrosion, aligning with the growing demand for environmentally friendly materials.
Building and Construction: IFR coatings can be applied to structural steel, wood, and other construction materials to improve fire resistance, crucial for commercial buildings, residential complexes, and infrastructure projects.
Technological Advancements: Incorporating nanotechnology and hybrid materials into IFR coatings enhances their performance, making them more effective at higher temperatures and improving their durability and aesthetic appeal. This innovation opens new applications and markets for these advanced coatings.