Synergistic effect of basalt fiber on the thermal properties of intumescent fire retardant coating
Author: Faiz Ahmad - March 2023
Muhammad Yasira, Norlaili Amira, Sami Ullahb, Maude Jimenez
Abstract
This research work presents the enhancement of thermal performance of intumescent fire-retardant coatings (IFRCs) to investigate the synergistic effects of novel type of fiber reinforcement (basalt fibers) towards heat shielding capability for steel structures. The coating basis consists of bisphenol-A epoxy resin (NPEL-128) cross-linked with polyamide amine (ACR Hardener (H-2310)), mixed with expandable graphite (EG), ammonium polyphosphate (APP), melamine and boric acid. Various formulations with different fiber loading were synthesized and characterized. Bunsen burner test in accordance to UL-1709 was performed to examine their fire retardant properties. Moreover, furnace test was carried out to investigate the char expansion. The results showed that 2 wt% basalt fibers (IFRC-B2) greatly enhanced the heat insulation performance, the steel plate backside temperature reaching 187o C after 1-h fire test compared to 375o C for the control formulation (CF) without fiber reinforcement. Char expansion measurements carried out after furnace test show that in the presence of basalt fibers the expansion of IFRC-B2 was twice that of CF. Char was also analyzed by Field Emission Scanning Electron Microscopy (FESEM). Micrographs revealed deep cracks on CF char surface, allowing the heat to diffuse more rapidly and explained the poor fire performances. The char of IFRC-B2 was smooth and dense, while distribution of basalt fibers and char cells were homogenous, with presence of small voids of about similar size, which limited heat transfers. Thermogravimetric analyses (TGA) in pyrolysis conditions showed that residual weight increases by 10 wt%, confirming the increase in thermal stability of the basalt containing formulation.
Methodology
Expandable graphite (EG) flakes were purchased from Analisa Resources Sdn. Bhd. Melamine (MEL) was provided by Chemolab supplies, boric acid (BA) was purchased from sigma-Aldrich (Malaysia) Sdn. Bhd. Ammonium polyphosphate (APP) was bought from Clarient (Malaysia) Sdn. Bhd. Epoxy resin bisphenol-A (NPEL128) and ACR hardener (H-2310) were supplied by WWRC (Malaysia) Sdn. Bhd. The sandblasted mild steel plates (50x50x1.5 mm3 ) and (100x100x1.5 mm3 ) were supplied from TSA industries Sdn. Bhd. All the ingredients were grinded in proper proportion and mixed together. Basalt fiber (6 mm length) was introduced in the IFRC formulation from 0.5 to 2 wt. %. The prepared formulations are shown in Table 1.
Impact & Benefits
Enhanced Fire Protection Performance: The addition of basalt fibers significantly improves the thermal resistance of the coating, leading to better protection of steel structures during a fire. The increased char expansion and improved char structure provide a more effective barrier against heat.
Structural Integrity:Basalt fibers enhance the integrity of the char formed during a fire, making it less likely to detach from the substrate. This ensures continuous protection throughout the duration of the fire.
Market Dynamics: With the forecasted market size of $1.25 billion USD for intumescent coatings by 2025, basalt fiber-reinforced IFRCs are well-positioned to capture a significant share due to their superior performance.
Improved Thermal Performance:The integration of basalt fibers into intumescent coatings results in a substantial increase in char expansion (double the char expansion of conventional formulations) and better thermal insulation, effectively protecting the steel substrate from heat.
Increased Residual Weight:The residual weight of the char is increased by 7% with the addition of basalt fibers, indicating a more substantial protective layer that remains intact during high-temperature exposure.
Durability and Longevity:Basalt fibers provide excellent corrosion and chemical durability, enhancing the lifespan and reliability of the fire protection system in harsh environments.
Synergistic Effects: The synergistic effects of basalt fibers with the existing components of the intumescent coating lead to overall improved performance, including better heat shielding and stability of the char at high temperatures.
Findings/Figures and Research Data
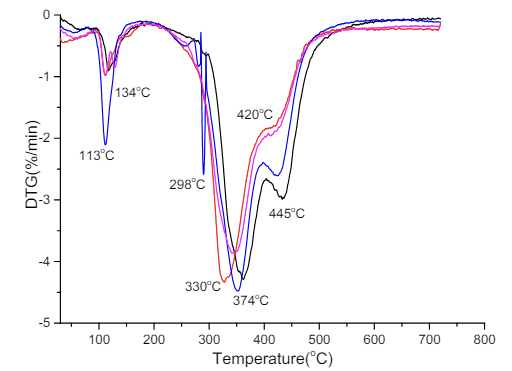
for IFRC-B1, 32.3% for IFRC-B1.5 and 33.7% for IFRC-B2, respectively. These results are presented in Figure 7. The residual weight was increased by the incorporation of basalt fiber in the intumescent coating formulations. As basalt fiber can withstand in 25-800°C range of temperature, it means that greater weight percentage of basalt fiber will hinder the decomposition of the intumescent coating formulations at this temperature range [14]. The residual weight of IFRC-B2 was best among all formulations. The DTG graph of IFRC-B2 is shown in Figure 8. There are four main degradation steps 134, 298, 374 and 445°C, respectively. The decomposition of boric acid starts at 134°C while EG, APP and epoxy decomposed at 298°C and 374°C, respectively. The boron phosphate is formed at 445°C [14]. It is evidenced that the addition of 3 wt. % of basalt fibers increased the thermal stability of IFRCs from 330 to 375°C as shown in Figure 8. The IFRCB2 have improved residual char among all formulations.
Market Potential
Current Market Size and Growth Trends: The market for passive fire protection systems, particularly for steel structures, is growing due to increasing safety regulations and awareness of fire hazards.
Unique Selling Points of Basalt Fiber-Reinforced IFRCs: Enhanced thermal resistance and structural integrity of the char compared to conventional intumescent coatings.
Applications and Industry Adoption: Sectors with stringent fire protection requirements, such as construction (particularly high-rise buildings and infrastructure), oil and gas, and transportation, are likely to be significant markets.
Competitive Landscape: Basalt fiber-reinforced IFRCs will compete with existing fire protection solutions like traditional intumescent coatings, fire walls, fire boards, and foams.
Regulatory and Safety Standards: Increased regulatory focus on fire safety in construction and industrial sectors can boost demand.