Synergistic effects of kaolin clay on intumescent fire retardant coating composition for fire protection of structural steel substrate
Author: Faiz Ahmad - March 2023
Abstract
Intumescent coating is an insulating material designed to decrease heat transfer to a substrate structure. This research presents the results of different formulations developed to study the effects of kaolin clay on expansion of coating and heat shielding during the fire test. The intumescent coating formulations (ICFs) were tested at 950 °C for 1 h. The results showed that the coatings were stable and well bound with substrate. The coatings were characterized by using Field emission scanning electron microscopy (FESEM), X-ray diffraction (XRD), Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), Thermogravimetric analysis (TGA) and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS). The morphology of char was studied by FESEM on the coating after fire test. XRD and FTIR showed the presence of carbon (graphite), boron phosphate, boron oxide, sassolite and kaolinite in the residual char. TGA showed that kaolin clay reinforced formulation; IF5-KC enhanced 49% residual weight than that of IF-Control formulation. XPS analysis showed that elemental composition of IF5-KC char residue gave 41.80% carbon content in the residual char. An accelerated weathering test ASTM D 6695-03 showed that IF5-KC coating sustained its integrity up to 90 days under accelerated weathering chamber.
Methodology
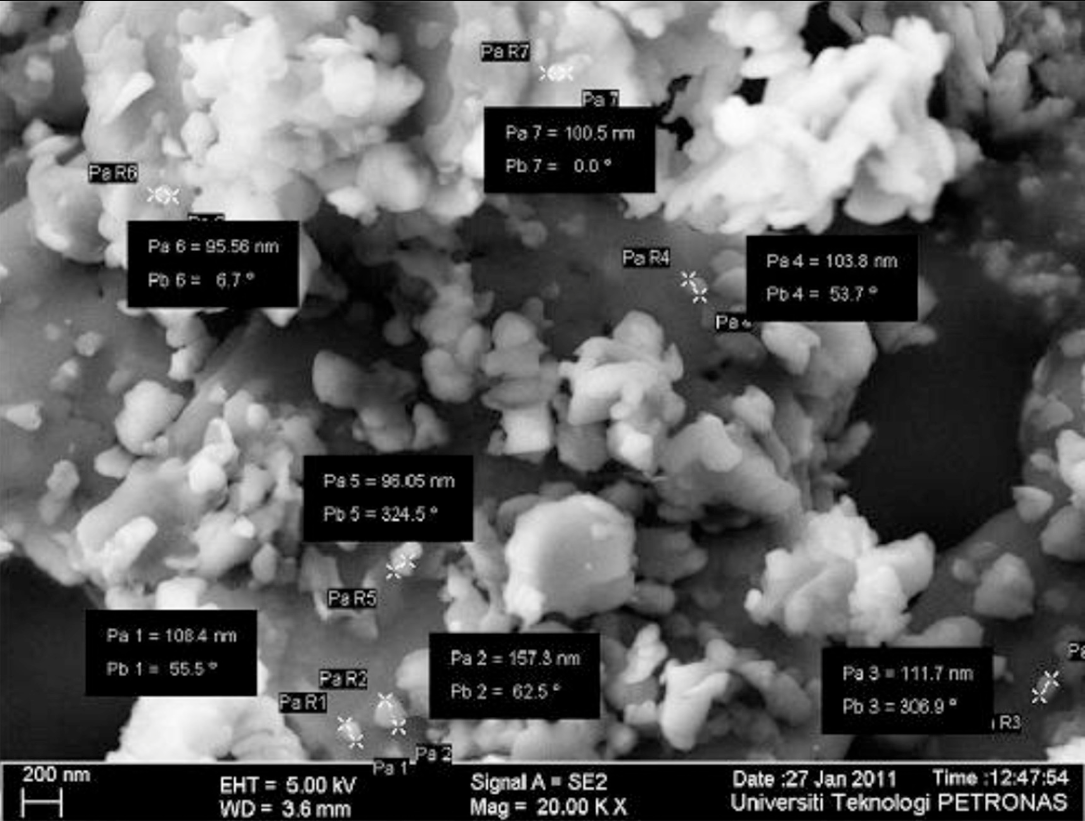
Kaolin clay was supplied from Jinyang Shanxi Jinyang Calcined kaolin Ltd. China. The Field Emission Scanning Electron Microscopy (FESEM) micrograph of kaolin clay is shows the particle size ranging in 60-150 nm with hexagonal shape in Fig. 1. Flake graphite, melamine (MEL) and boric acid (BA) were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich (M) Sdn Bhd. Malaysia. Ammonium polyphosphate (APP) was provided by Clariant (Malaysia) Sdn Bhd. Binder system bisphenol A epoxy resin BE-188 (BPA) and ACR Hardener H-2310 polyamide amine were supplied by Mc-Growth chemical Sdn Bhd. Malaysia. Structural steel A36M was provided by TSA industries (Ipoh) Sdn. Bhd. Malaysia.
Impact & Benefits
Improved Thermal Barrier: Kaolin clay significantly enhances the performance of intumescent fire retardant coatings by forming a more robust and effective char layer. This char layer acts as an insulating barrier, reducing the rate of heat transfer to the protected substrate.
Extended Structural Integrity: By maintaining the structural integrity of materials under high temperatures for longer periods, kaolin-enhanced coatings provide crucial time for evacuation and fire control, potentially saving lives and reducing property damage.
Chemical Reactions: Kaolin clay, when combined with other additives like expandable graphite, improves the formulation's fire retardant properties by participating in synergistic chemical reactions that enhance the stability and efficacy of the char layer.
Enhanced Performance: The synergistic effects lead to a more efficient flame retardant system, which can achieve higher performance standards with potentially lower quantities of each individual component.
Retention of Material Properties: Experiments have shown that kaolin clay additives do not degrade the overall properties of the base material, ensuring that the mechanical and aesthetic properties of the coated materials are preserved.
Sustainability: The use of kaolin clay in fire retardant formulations aligns with environmental sustainability goals by minimizing the release of harmful substances during fires.
Findings/Figures and Research Data
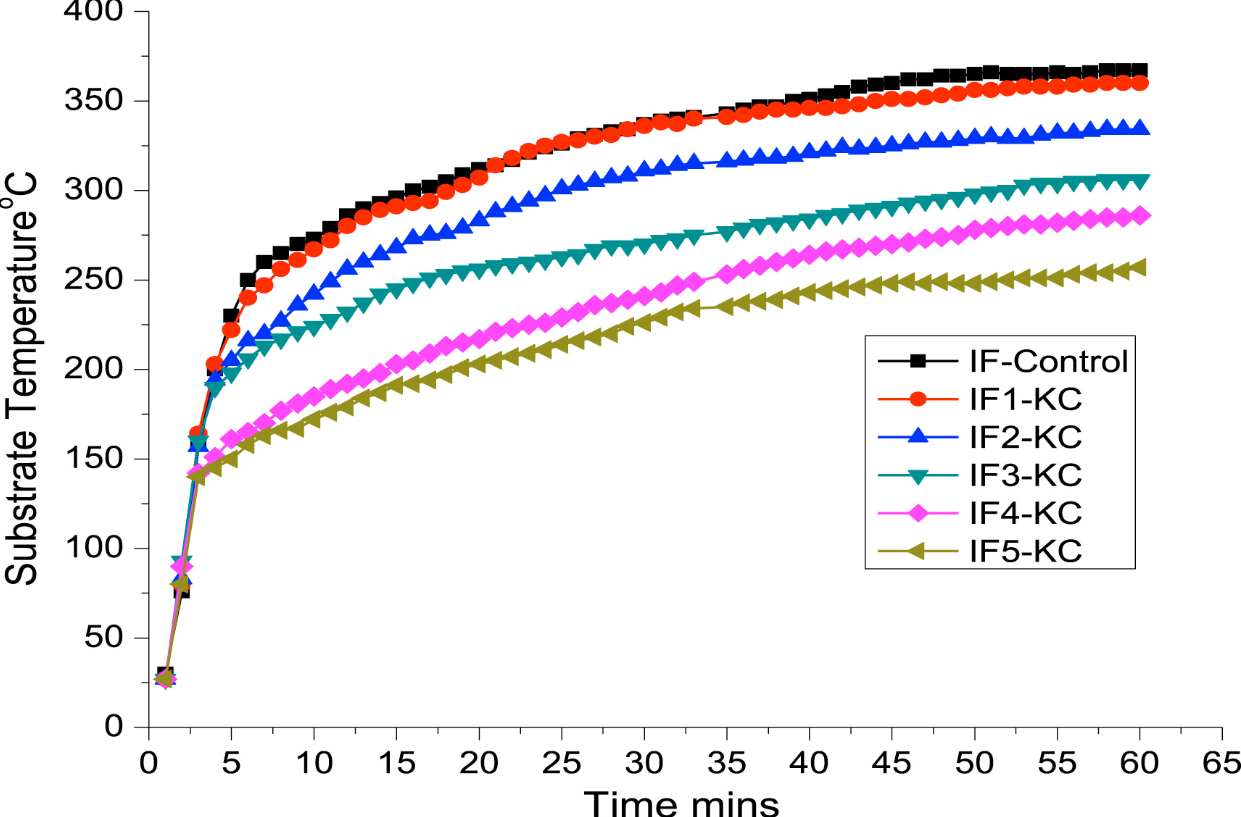
The multiparous can minimize heat transferred to the substrate, and protect the substrate. Rate of heat transfer through the char layer depends on the heat resistant of the substrate to fire. The expansion of the char and its structure are very important to common fire resistant properties of coating. The time versus substrate temperature curves are shown in Fig. 2, expansion of char is presented in Fig. 3, and the char photographs of IF4-KC and IF5-KC after fire test are shown in Fig. 4.
Market Potential
Growing Awareness and Regulatory Pressure: Increasingly stringent fire safety regulations and building codes globally are pushing for the adoption of advanced fire retardant materials.
Construction and Infrastructure Development: Rapid urbanization and the consequent construction boom are leading to higher demand for fire-resistant materials.
Technological Advancements: Advances in material science are facilitating the development of more effective and efficient fire retardant coatings.
End-Use Industries: Manufacturing facilities, warehouses, and chemical plants where fire hazards are significant.
Sustainability: Growing demand for environmentally friendly fire retardant materials that do not release toxic fumes during combustion.